Posts Tagged ‘NEWSWEEK’
AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AFGHANISTAN, ALEX PRETTI, ALLEN DULLES, ALTERNET, AMAZON, AMERICABLOG, ANTI-CASTRO CUBANS, AP, APPLE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, ASSASSINATION, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BARACK OBAMA, BARI WEISS, BAY OF PIGS, BBC, BIG TECH, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BUZZFEED, CANADA, CANADIANS, CARLOS MARCELLO, CBS NEWS, CIA, CITIENSHIP TESTS, CIVIL RIGHTS, CLEAR AND PRESENT DANGER (FILM), CNN, COLUMBIAN/MEXICAN DRUG CARTELS, CONSPIRACIES, CROOKS AND LIARS, CUBA, CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS, CUSTOMS AND BORDER PATROL (CBP), DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, FBI, FBI AGENTS, FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL RESERVE, FEDERAL TRADE COMMISSION, FIDEL CASTRO, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAZA, GOOGLE, GREENLAND, GREENLANDERS, GUN RIGHTS ENTHUSIASTS, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HARRISON FORD, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, IMMIGRANTS, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), INSPECTORS GENERAL, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, IRAN, IRANIANS, ISLAM, ISRAEL, ISREAL, J. EDGAR HOOVER, JAIME DIMON, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JEFF BEZOS, JEFFREY, JEFFREY EPSTEIN, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN F. KENNEDY, JOHN KELLY, JOURNALISTS, JP MORGAN CHASE, JUSTICE DEPARTMENT PROSECUTORS, Kamala Harris, KGB, LAWYERS, LEBANON, LETITIA JAMES, MAFIA, MARCUS AURELIUS, MARINE BARRACKS BOMBING, MARK ESPER, MARK MILLEY, MEDAL OF HONOR WINNERS, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICARE, MELANIA TRUMP, META, MICHELLE OBAMA, Military, MINNESOTA, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUSLIMS, NATIONAL RIFLE ASSOCIATION (NRA), NATO, NAVAJO CODE TALKERS, NBC NEWS, NERO, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, NUCLEAR REACTOR SITES, NUCLEAR TEST BAN TREATY, NUCLELAR TEST BAN TREATY, OIL MILLIONAIRES, PAKISTAN, PAM BONDI, PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, PBS NEWSHOUR, PETE HEGSETH, POLICE, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RARE EARTH MIINERALS, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, Ronald Reagan, RUDY GIULIANI, SALON, SAM GIANCANA, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOMALIS, SOUTHERN RACISTS, SOVIET UNION, SUICIDE BOMBINGS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, TARIFFS, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE KENNEDY HALF-CENTURY (BOOK), THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE MILITARY, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE PRINCE (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIM COOK, TIME, TRAJAN, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, WATERGATE, X
In Bureaucracy, Business, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Medical, Military, Politics, Social commentary on February 17, 2026 at 12:12 am
Just as President John F. Kennedy was passionately loved and hated, so, too, is Donald J. Trump. And Trump, at 79, has already been the target of two assassination attempts.

Donald Trump
Among the reasons why Trump is so widely hated:
- Gun rights enthusiasts – After Customs and Border Patrol (CBP) agents shot intensive care nurse Alex Pretti on January 24, Trump criticized Pretti for carrying a licensed, concealed pistol: “You can’t have guns, you can’t walk in with guns. I don’t like that he had a gun. I don’t like that he had two fully loaded magazines. That’s a lot of bad stuff.”
- The National Rifle Association (NRA) called Trump’s comments “dangerous and wrong.” And the National Association for Gun Rights (NAGR) stated: “Carrying an extra magazine implies nothing. Claiming otherwise sets a dangerous precedent for Second Amendment rights and creates an easy backdoor argument for magazine bans and similar legislation.”

Alex Pretti
- The military – Following his anti-DEI executive order, the Department of Defense deleted content that included the achievements of nonwhite servicemen and women—such as Navajo code talkers, black Tuskegee Airmen, Medal of Honor winners and women veterans. High-ranking militar y leaders fear retribution and the politicization of the armed forces.
- Former high-profile military leaders, including former Chiefs of Staff John Kelly and Mark Milley and former Defense Secretary Mark Esper, have criticized Trump, with some describing him as a ‘fascist to the core” and a threat to democracy.
- Trump has deployed the National Guard to Democratic cities against the wishes of their states’ governors.
- In September, 2025, Trump and Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth aired grievances to a silent, uncomfortable audience of top military leaders.
- Canadians – Trump has imposed 25% tariffs on Canadian goods, covering major sectors like steel, aluminum, and autos.
- And he has threatened to impose 100% tariffs due to trade disputes. These have caused significant anxiety regarding the Canadian economy, which relies heavily on trade with the United States.
- He has also repeatedly threatened to militarily invade Canada and make it the 51st state. Many Canadians feel betrayed by the treatment of a longstanding, peaceful ally, with 59% of Canadians now viewing the United States as their top threat.
- Greenlanders – Trump has grown increasingly bellicose about acquiring Greenland—by purchase or conquest. The official reason given: The dangers of Chinese or Russian conquest of the island, where the United States has an active military base for missile warning, defense and space surveillance.
- The real reason: To gain total access to Greenland’s rare earth minerals. This despite Greenland’s being a self-governing, autonomous part of the Kingdom of Denmark. The united States has recognized Denmark’s ties to Greenland since 1917 and signed a joint defense agreement in 1951.

Greenland
- Secret Service agents – There has never been a case of a Secret Service agent assassinating a President. But there are historical precedents for bodyguards turning on those they are supposed to protect. On January 22, 41 A.D. Cassius Chaerea and several other bodyguards hacked Roman Emperor Gaius Caligula to death with swords before other guards could save him.
- Caligula had often taunted Chaerea for having a weak voice. Similarly, Trump has forced Secret Service agents to work without pay through two major government shutdowns—for 35 days in 2018-19 and 43 days in 2025. Secret Service agents had to worry about meeting their bills and the needs of their families.
- Many agents could have friends or family members whose lives have been shattered by Trump’s massive layoffs of government employees and/or his assaults on the American medical establishment.
- Wall Street executives – For Trump’s attacks on Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell and public criticism of the Fed, which threaten the independence of the institution and the stability of the economy.
- And for suing JP Morgan Chase and its CEO Jamie Dimon for $5 billion, alleging the bank “debanked” him after the January 6, 2021 Capitol attack.
- Major investors and CEOs fear that Trump’s tariff policies will ignite a global crash—as happened in April ,2025.
- Iranians – For his scrapping the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), commonly known as the Iran nuclear deal.
- And for re-imposing “highest-level” economic sanctions on Iran, targeting critical sectors such as oil, finance and shipping.
- Nor will Iranians forgive him for ordering the June 21, 2025, bombing of three key Iranian nuclear sites: Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan.
- Barons of Columbian/Mexican drug cartels – For threatening to invade Columbia and Mexico and directly attack the drug lords who feed America’s demand for cocaine.
- This scenario forms the plot of the 1994 thriller, “Clear and Present Danger,” starring Harrison Ford. The movie ends with the American force almost wiped out by a drug lord’s army and being forced to evacuate Columbia.

Columbian drug lords
- Journalists – For his repeatedly attacking the nation’s free press as “the enemy of the people” for reporting his growing list of crimes and disasters.
- And barring the Associated Press from the White House for refusing to call the Gulf of Mexico “the Gulf of the United States.”
- Jeff Bezos, the CEO of Amazon, bought the Washington Post—which played a pivotal role in uncovering Watergate—-in 2013 and has turned that once-respected newspaper into a Right-wing cheerleader.
- And CBS News is now being rigorously censored by Editor-in-Chief Bari Weiss, a notorious Trump ally.
AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AFGHANISTAN, ALEX PRETTI, ALLEN DULLES, ALTERNET, AMAZON, AMERICABLOG, ANTI-CASTRO CUBANS, AP, APPLE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, ASSASSINATION, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BARACK OBAMA, BARI WEISS, BAY OF PIGS, BBC, BIG TECH, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BUZZFEED, CANADA, CANADIANS, CARLOS MARCELLO, CBS NEWS, CIA, CITIENSHIP TESTS, CIVIL RIGHTS, CLEAR AND PRESENT DANGER (FILM), CNN, COLUMBIAN/MEXICAN DRUG CARTELS, CONSPIRACIES, CROOKS AND LIARS, CUBA, CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS, CUSTOMS AND BORDER PATROL (CBP), DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, FBI, FBI AGENTS, FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL RESERVE, FEDERAL TRADE COMMISSION, FIDEL CASTRO, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAZA, GOOGLE, GREENLAND, GREENLANDERS, GUN RIGHTS ENTHUSIASTS, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HARRISON FORD, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, IMMIGRANTS, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), INSPECTORS GENERAL, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, IRAN, IRANIANS, ISLAM, ISRAEL, ISREAL, J. EDGAR HOOVER, JAIME DIMON, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JEFF BEZOS, JEFFREY, JEFFREY EPSTEIN, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN F. KENNEDY, JOHN KELLY, JOURNALISTS, JP MORGAN CHASE, JUSTICE DEPARTMENT PROSECUTORS, Kamala Harris, KGB, LAWYERS, LEBANON, LETITIA JAMES, MAFIA, MARCUS AURELIUS, MARINE BARRACKS BOMBING, MARK ESPER, MARK MILLEY, MEDAL OF HONOR WINNERS, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICARE, MELANIA TRUMP, META, MICHELLE OBAMA, Military, MINNESOTA, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUSLIMS, NATIONAL RIFLE ASSOCIATION (NRA), NATO, NAVAJO CODE TALKERS, NBC NEWS, NERO, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, NUCLEAR REACTOR SITES, NUCLEAR TEST BAN TREATY, NUCLELAR TEST BAN TREATY, OIL MILLIONAIRES, PAKISTAN, PAM BONDI, PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, PBS NEWSHOUR, PETE HEGSETH, POLICE, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RARE EARTH MIINERALS, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, Ronald Reagan, RUDY GIULIANI, SALON, SAM GIANCANA, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOMALIS, SOUTHERN RACISTS, SOVIET UNION, SUCIDE BOMBINGS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, TARIFFS, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE KENNEDY HALF-CENTURY (BOOK), THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE MILITARY, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE PRINCE (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIM COOK, TIME, TRAJAN, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, WATERGATE, X
In Bureaucracy, Business, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Medical, Military, Politics, Social commentary on February 16, 2026 at 12:55 am
The 2013 book, The Kennedy Half-Century: The Presidency, Assassination and Lasting Legacy of John F. Kennedy, offers a truly astounding chapter.
Its early chapters provide an overview of the major events of the brief Kennedy administration: “The Torch Is Passed,” “Steel at Home and Abroad,” “Europe, Space and Southeast Asia.”
The next chapters concentrate on the assassination: “Echoes From Dealey Plaza,” “Questions, Answers, Mysteries,” “Rounding Up the Usual Suspects,” “Examining the Physical Evidence.”
For anyone who’s previously delved into the thousand days of the Kennedy administration, much of these subjects will be at least generally familiar. But Chapter 11 zooms into an area that might seem right out of The Twilight Zone: “Inevitability: The Assassination That Had to Happen.”

The chapter opens: “It has taken fifty years to see part of the truth clearly: John F. Kennedy’s assassination might have been almost inevitable. It didn’t have to happen on November 22, 1963, but given a host of factors, one could reasonably argue that JFK was unlikely to make it out of his Presidency alive.”
Among the “host of factors” who had reason to hate Kennedy:
- New Orleans Mafia boss Carlos Marcello – Furious over the crackdown on organized crime by JFK’s brother, Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy, he spoke of having the President assassinated to render RFK impotent.
- Anti-Castro Cubans – Enraged at Kennedy’s failure to overthrow Cuban dictator Fidel Castro after landing 1,700 armed Cuban exiles at the Bay of Pigs.
- James R. Hoffa – Pursued relentlessly by Robert Kennedy, the president of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters Union talked privately of having the Attorney General assassinated.
- The KGB – For Kennedy’s humiliating the Soviet Union during the Cuban Missile Crisis.
- Chicago Mafia boss Sam Giancana – Expecting to win immunity from federal prosecution, he fixed the 1960 Illinois election for John F. Kennedy. Instead, he found himself under intense investigation by RFK’s Justice Department—and raged that the Kennedys had “welshed” on their part of the deal.
- FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover – Fearing dismissal by the Kennedys, he withheld lethal threats his agents overheard when bugged Mafiosi railed against the President and Attorney General.

J. Edgar Hoover
- Southern racists – Who believed that JFK was a “nigger lover” for supporting civil rights for blacks. Especially after he sent deputy U.S. marshals and National Guardsmen to desegregate the University of Mississippi and, later, the University of Alabama.
- The CIA – Blamed by Kennedy for failing to overthrow Castro at the Bay of Pigs, its legendary director, Allen Dulles, was forced to resign. Many of its agents blamed JFK for refusing to commit American military forces during that attack—and laying the seeds for the Cuban Missile Crisis.
- Military and defense establishment – Appalled by Kennedy’s “weak” response to the Cuban Missile Crisis and support of the Nuclear Test Ban Treaty with the Soviet Union.
- Fidel Castro – Enraged by a series of CIA-Mafia attempts on his life, he publicly warned: “U.S. leaders should think if they are aiding terrorist plans to eliminate Cuban leaders they themselves will not be safe.”

Fidel Castro
Just as President Kennedy was passionately loved and hated, so, too, is Donald J. Trump. And Trump, at 79, has already been the target of two assassination attempts.

Donald Trump
Among the “host of factors” who have reason to hate Trump:
- Blacks – For his racist attacks on Barack and Michelle Obama and on black journalists, politicians and celebrities.
- His issuing executive orders to eliminate diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) programs—and remove references to black historical figures from government websites.
- A major reason for his flooding Minnesota with 3,000 ICE agents: Its large Somali population, which he publicly labeled “garbage.”
- Hispanics – For turning them into the #1 target of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). Throughout 2025, ICE arrested nearly 300,000 to 328,000 people, the vast majority of them Hispanics. These included not only illegal aliens but those with green cards awaiting their processing as citizens.
- More than 70,000 migrants are now held in detention centers. ICE vows to detain an additional 80,000 people in them. Some centers will reportedly hold up to 10,000 detainees apiece. This will allow Trump to imprison and then deport vastly more people much more quickly.
- Muslims – He’s said “I think Islam hates us” and called for a “total and complete shutdown of Muslims entering the United States.”
- And he’s imposed a travel ban on 11 Islamic countries in the Middle East, North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
- He’s proposed a registry for American Muslims and expressed support for surveillance of mosques.
- And he’s sided with Israel in its military attacks on Gaza and Iran.
- Police officers – Despite his claiming to be a “law and order” President, Trump pardoned more than 1,500 of his supporters who had attacked Capitol Police on January 6, 2021. More than 140 police officers were injured.
- In November 2025, he issued preemptive pardons for 77 people involved in the plot to overturn the 2020 election results, including Rudy Giuliani and Mark Meadows.
- Among the convicted drug kingpins serving life sentences he has pardoned: Andre Donnell Routt, Zechariah Benjamin, Joe Angelo Sotelo, Edward Ruben Sotelo and Larry Hoover.
ABC NEWS, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BLOOMBERG NEWS, BLUESKY, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CHRISTOPHER DORNER, CNN, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DEATH THREATS, FACEBOOK, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GEORGE ZIMMERMAN, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HAWAII FIVE-O, HUFFINGTON POST, JACK LORD, LORI TANKEL, LOS ANGELES POLICE DEPARTMENT, MEDIA MATTERS, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLICE, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROBERT DALEY, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SWAT TEAMS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, TARGET BLUE, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE UNTOUCHABLES, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WALL STREET JOURNAL, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRAYVON MARTIN, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UPI, USA TODAY, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on February 13, 2026 at 12:10 am
Lori Tankel had a problem: A lot of angry people thought she was George Zimmerman.
She began getting death threats on her
Unfortunately for Tankel, her number was one digit away from the number Zimmerman used to make his call to police just before he fatally shot Martin.
That phone number had been shown throughout the trial. And, believing the number was Zimmerman’s, someone posted Tankel’s number online.
Just minutes after the verdict, Tankel began getting death threats. “We’re going to kill you. We’re going to get you. Watch your back,” threatened a typical call.

George Zimmerman
Tankel worked as a sales representative for several horse companies. She had grown used to relying on her phone to keep her business going.
But, almost as soon as the Zimmerman verdict came in, “My phone just started to blow up. Phone call after phone call, multiple phone
So she did what any ordinary citizen, faced with multiple death threats, would do: She called the police.
According to her, the Seminole County Sheriff’s Office told her the department itself receives around 400 death threats a minute on social media sites.
In short: Unless you’re wealthy, a politician or—best of all, a cop—don’t expect the police to protect you if your life is threatened.
First, above everyone else, police look out for each other.
Robert Daley bluntly revealed this truth in his 1971 bestseller, Target Blue: An Insider’s View of the N.Y.P.D. A police reporter for the New York Times, he served for one year as a deputy police commissioner.

“A great many solvable crimes in the city were never solved, because not enough men were assigned to the case, or because those assigned were lazy or hardly cared or got sidetracked,” wrote Daley.
“But when a cop got killed, no other cop got sidetracked. Detectives worked on the case night and day….
“In effect, the citizen who murdered his wife’s lover was sought by a team of detectives, two men. But he who killed a cop was sought by 32,000.”
That’s why the Mafia tried to bribe cops, but never killed them.
Second, don’t expect the police to do for you what they’ll do for one another.
In February, 2013, Christopher Dorner declared war on his former fellow officers of the Los Angeles Police Department.
The LAPD assigned security and surveillance details to at least 50 threatened officers and their families. A typical detail consists of two to five or more guards. And those guards must be changed every eight to 12 hours.

Those details stayed in place long after Dorner was killed in a firefight on February 12, 2013.
But if your bullying neighbor threatens to kill you, don’t expect the police to send a guard detail over. They’ll claim: ”We can’t do anything until the guy does something. If he does, give us a call.”
Third, the more status and wealth you command, the more likely the police are to address your complaint or solve your case.
If you’re rich, your complaint will likely get top priority and the best service the agency can provide. In Boston, such cases are known as “Red balls.”
But if you’re poor or even middle-class without high-level political or police connections, you’ll be told: “We just don’t have the resources to protect everybody.”
Fourth, don’t expect your police department to operate with the vigor or efficiency of TV police agencies.
“I want this rock [Hawaii] sealed off,” Steve McGarrett (Jack Lord) routinely ordered when pursuing criminals on “Hawaii Five-O.”

Jack Lord as Steve McGarrett
Real-life police departments, on the other hand:
- Often lack state-of-the-art crime labs to analyze evidence.
- Often lose or accidentally destroy important files.
- Are—like all bureaucracies—staffed by those who are lazy, indifferent or incompetent.
- Are notoriously competitive, generally refusing to share information with other police departments-–thus making it easier for criminals to run amok.
Even when police ”solve” a crime, that simply means making an arrest. After that, there are at least three possible outcomes:
- The District Attorney may decide not to file charges.
- The perpetrator may plead to a lesser offense and serve only a token sentence—or none at all.
- He might be found not guilty by a judge or jury.
Fifth, the result of all this can only be increased disrespect for law enforcement from a deservedly—and increasingly—cynical public.
It is the witnessing of blatant inequities and hypocrisies such as those displayed in the Christopher Dorner case that most damages public support for police at all levels.
When citizens believe police lack the ability—or even the will—to protect them or avenge their victimization, that is a deadly blow to law enforcement.
Police depend on citizens for more than crime tips.
They depend upon them to support hiring more cops and buying state-of-the-art police equipment.
When public support vanishes, so does much of that public funding.
The result can only be a return to the days of the lawless West, where citizens—as individuals or members of vigilante committees—look only to themselves for protection.
ABC NEWS, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG NEWS, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, CNN, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DECEIT, DETECTIVES, FACEBOOK, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HUFFINGTON POST, INTERROGATION, INTERVIEWING, LIE DETECTORS, MEDIA MATTERS, MIRANDA VS. ARIZONA, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLICE, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, POLYGRAPH, PROSECUTION, RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SUPREME COURT, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE DENVER POST, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WALL STREET JOURNAL, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UPI, USA TODAY, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on February 12, 2026 at 12:10 am
Ever heard of “polygraph by copier”?
If you haven’t, here’s how it works:
A detective loads three sheets of paper into a Xerox machine.
“Truth” has been typed onto the first sheet.
“Truth” has been typed onto the second sheet.
“Lie” has been typed onto the third sheet.

Then a criminal suspect is led into the room and told to put his hand against the side of the machine.
“What is your name?” asks the detective.
The suspect gives it.
The detective hits the copy button, and a page comes out: “Truth.”
“Where do you live?” asks the detective.
The suspect gives an address, the detective again hits the copy button, and a second page appears: “Truth.”
Then comes the important question: “Did you kill Big Jim Tate on the evening of….?”
The suspect answers. The detective presses the copy button one last time, and the sheet appears: “Lie.”
“Well, well, well, you lying little bastard,” says the detective.
Convinced that the police have found some mysterious way to peer into the darkest recesses of his criminality, the suspect “gives it up” and makes a full confession.
Yes, contrary to what many believe, police can legally use deceit to obtain a confession.
In 1973, the Supreme Court ruled, in United States v. Russell: “Nor will the mere fact of deceit defeat a prosecution, for there are circumstances when the use of deceit is the only practicable law enforcement technique available.”
In that case, the Court narrowly upheld a conviction for methamphetamine production even though the defendant had argued entrapment.
So what types of interrogative deceit might a police officer use to develop admissible evidence of a suspect’s guilt?

Police interrogation
The general rule is that deception can be used so long as it’s not likely to cause an innocent person to commit a crime or confess to a crime that s/he didn’t commit.
Consider the following examples:
- A detective is interviewing a suspect in a rape case. “Oh, that girl,” he says, thus implying that the victim was a slut and had it coming. The suspect, thinking he’s dealing with a sympathetic listener, starts bragging about his latest conquest—only to learn, too late, that his listener isn’t so simpatico after all.
- “We found your prints on the gun”—or on any number of other surfaces. Actually, there are few good places on a pistol to leave prints. And those that are left can be smeared. The same goes for other surfaces. But if a suspect can be led to believe the cops have his prints, a confession is often forthcoming.
- A police officer is interrogating a suspect in a murder case. “He came at you, didn’t he?” asks the cop. The suspect, who murdered the victim in cold blood, thinks he has an escape route. “Yeah, he came at me”—this confirming that, yes, he did kill the deceased.
- “Your partner just gave you up” is a favorite police strategy when there is more than one suspect involved. If one suspect can be made to “flip”—turn–-against the other, the case is essentially wrapped up.

- Interrogating a bank robbery suspect, a cop might say: “We know you didn’t do the shooting, that you were only the wheelman.” This implies that the penalty for driving the getaway car is far less than that for killing someone during a robbery. In fact, criminal law allows every member of the conspiracy to be charged as a principal.
- “I don’t give a damn what you did,” says the detective. “Just tell me why you did it.” For some suspects, this offers a cathartic release, a chance to justify their guilt.
- The “good cop/bad cop” routine is known to everyone who has ever seen a police drama. Yet it continues to yield results so often it continues to be routinely used. “Look, I believe you,” says the “good” cop, “but my partner’s a real asshole. Just tell me what happened so we can clear this up and you can go.”
- “So,” says the detective, “why do you think the police believe you did it?” “I have no idea,” says the suspect, confident that he isn’t giving up anything that might come back to haunt him. “Well,” says the cop, “I guess you’ll just have to make something up.” Make something up sounds easy, but it’s actually a trap. The suspect may end up giving away details that could incriminate him—or lying so brazenly that his lies can be used against him.
So is there a best way for a suspect to deal with an invitation to waive his Miranda right to remain silent?
Yes, there is. It’s to refuse to say anything and to ask for permission to call a lawyer.
That’s the preferred method for Mafia hitmen—and accused police officers.
Any cop who finds himself under investigation by his department’s Internal Affairs unit automatically shuts up—and calls his lawyer.
Contrary to popular belief, an arrestee is allowed to make more than one phone call in most states.
Any other reason—no matter how well-intentioned—may well result in a lengthy prison sentence.
ALEX PRETTI, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CESARE BORGIA, CNN, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GREGORY BOVINO, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HUFFINGTON POST, KAROLINE LEAVITT, KRISTI NOEM, MEDIA MATTERS, MINNESOTA, MINNIEAPOLIS, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NBC NEWS, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI, NPR, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRINCE (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TODD BLANCE, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CUSTOMS AND BORDER PATROL, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY, UPI, USA TODAY, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on February 11, 2026 at 12:10 am
On January 24, 2026, Alex Jeffrey Pretti, a 37-year-old American intensive care nurse for the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, was shot multiple times and killed by agents of United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Pretti was filming law enforcement agents with his phone attacking Minnesota residents. At one point, he stood between an agent and a woman whom the agent had pushed to the ground, putting his arm around her.
Pretti reached to wrap his arms around the fallen woman, apparently trying to help her up.

Alex Pretti
An agent shoved Pretti, and Pretti and the woman fell, still embracing. He was then pepper-sprayed and wrestled to the ground by several federal agents. Both of his arms were pinned down by his head. The agent that pepper-sprayed Pretti hit him with the pepper spray canister multiple times.
Pretti was legally licensed to carry a handgun, and was wearing one in a holster on his hip. An agent removed Pretti’s firearm. Another agent heard someone yell “Gun!” He drew his pistol and shot Pretti at close range.
The shooter was standing behind Pretti and not under direct threat, but fired three more shots into Pretti’s back, as he lay on the pavement with one hand still holding his phone and his other hand holding his glasses.
The agent who pepper-sprayed Pretti took out his gun and, together with the first shooter, fired six more shots at Pretti as he lay motionless on the ground.
The two agents fired a total of 10 shots in five seconds.

The killing of Alex Pretti ignited a firestorm of anger and horror throughout the country against the Trump administration. Protests were held in Seattle, Washington; Portland, Oregon, Durham, North Carolina, Oak Park, Illinois, Los Angeles and Boston.
Arousing even greater fury were inflammatory and slanderous accusations made against Pretti by Trump administration officials.
“He was there to perpetuate violence, and he was asked to show up and to continue to resist by a governor who’s irresponsible and has a long history of corruption and lying, and we won’t stand for it anymore,” said Secretary of Department of Homeland Security Kristi Noem.
Noem did not offer any evidence to back up her slander.

Kristi Noem
And White House Deputy Chief of Staff Stephen Miller called Pretti “a domestic terrorist who tried to assassinate law enforcement.”
Like Noem, Miller did not offer any evidence to support his slander.
Bystander video verified and reviewed by Reuters, the BBC, The Wall Street Journal and the Associated Press gave the lie to the Trump administration’s attacks on Pretti.
Faced with overwhelming—and video—evidence that Pretti had been shot while helplessly pinned to the ground, Trump officials started backpeddling.
“I don’t think anybody thinks that they were comparing what happened on Saturday to the legal definition of domestic terrorism,” said Deputy Attorney General Todd Blanche on Fox News.
“I have not heard the president characterize Mr Pretti in that way [as a domestic terrorist]” said White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt.
The ultimate pullback (so far) by the Trump administration was the demotion of Gregory Bovino, commander-at-large of the Border Control in Minneapolis.
Bovino had become the face of ICE brutality—ICE agents using tear gas against peaceful protesters, battering down a door to enter a house, smashing car windows and dragging people from vehicles.
Bovino had stated that Pretti intended to inflict “maximum damage and massacre law enforcement.”
On January 26, two days after Pretti’s death, Bovino was dismissed as commander-at-large and returned to El Centro, California.
More than 500 years ago, Niccolo Machiavelli, the father of modern political science, outlined how tyrants try to deflect public anger against the agents they appointed.
In Chapter Seven of The Prince, he writes:
“When the duke [Cesare Borgia] occupied the Romagna he found it under the rule of weak masters, who rather plundered their subjects than ruled them, and gave them more cause for disunion than for union.
“The country was full of robbery, quarrels, and every kind of violence; and so, wishing to bring back peace and obedience to authority, he considered it necessary to give it a good governor. Thereupon he promoted Messer Ramiro d’Orco [de Lorqua], a swift and cruel man, to whom he gave the fullest power.
“This man in a short time restored peace and unity with the greatest success. Afterwards the duke considered that it was not advisable to confer such excessive authority, for he had no doubt but that he would become odious.
“And because he knew that the past severity had caused some hatred against himself….he desired to show that, if any cruelty had been practiced, it had not originated with him, but in the natural sternness of the minister.
“Under this pretense he took Ramiro, and one morning caused him to be executed and left on the piazza at Cesena with the block and a bloody knife at his side. The barbarity of this spectacle caused the people to be at once satisfied and dismayed.”
The Trump administration’s pullback proves that what Machiavelli wrote 500 years ago remains entirely relevant today.
ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALEX PRETTI, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG NEWS, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CNN, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GREGORY BOVINO, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HUFFINGTON POST, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), JACOB FREY, JOHN STEINBECK, MEDIA MATTERS, MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NORWAY, NPR, PAM BONDI, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAW STORY, RENEE GOOD, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOCRATES, ST. PAUL, TALKING POINTS MEMO, TERRORISM, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE MOON IS DOWN (BOOK), THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIM WALZ, TIME, TODD BLANCHE, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UPI, USA TODAY, WORLD WAR11
In History, Military, Politics, Social commentary on February 10, 2026 at 12:10 am
With Minnesota under siege by brutal and murderous agents of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) this is an appropriate time to read John Steinbeck’s 1942 novel, The Moon Is Down.
Written to inspire resistance movements in occupied countries, it has appeared in at least 92 editions across the world.
It tells the story of a Norwegian village occupied by Germans in World War II.
At first the invasion goes swiftly. Wehrmacht Colonel Lanser establishes his headquarters in the house of the democratically-elected Mayor Orden.
Lanser, a veteran of World War I, considers himself a man of civility and law. But in his heart he knows that “there are no peaceful people” when their freedom has been forcibly violated.

After an alderman named Alex Morden is executed for killing a German officer, the townspeople settle into “a slow, silent waiting revenge.”
Between the winter cold and the hostility of the townspeople, the Germans become fearful and disillusioned. One night, a frightened Lieutenant Tonder asks: “Captain, is this place conquered?”
“Of course.”
“Conquered and we’re afraid; conquered and we’re surrounded,” replies Tonder, hysterically. “Flies conquer the flypaper. Flies capture two hundred miles of new flypaper!”
Several nights later, Tonder knocks at the door of Molly Morden. He doesn’t realize that she nurses a deep hatred of Germans for the execution of her husband, Alex. Tonder desperately wants to escape the fury and loneliness of war. Molly agrees to talk with him, but insists that he leave and return another time.
When he returns the next evening, Molly invites him in—and then kills him with a pair of scissors.

John Steinbeck
A British plane flies over the town and drops packages of dynamite, which the townspeople hurriedly collect.
When the Germans learn about the droppings, Colonel Lanser arrests Mayor Orden and Doctor Albert Winter. As the two await their uncertain future, Orden tries to remember the speech Socrates delivered before he was put to death:
“Do you remember in school, in the Apology? Socrates says, ‘Someone will say, ‘And are you not ashamed, Socrates, of a course of life which is likely to bring you to an untimely end?’ To him I may fairly answer, ‘There you are mistaken: a man who is good for anything ought not to calculate the chance of living or dying; he ought only to consider whether he is doing right or wrong.’”
Colonel Lanser enters the room and warns Orden: “If you don’t urge your people to not use the dynamite, you will be executed.”
And Orden replies: “Nothing can change it. You will be destroyed and driven out. The people don’t like to be conquered, sir, and so they will not be. Free men cannot start a war, but once it is started, they can fight on in defeat.
“Herd men, followers of a leader, cannot do that, and so it is always the herd men who win battles and the free men who win wars. You will find that it is so, sir.”
Explosions begin erupting throughout the town.
As Orden is led outside—to his execution—he tells Winter, quoting Socrates: “’Crito, I owe a cock to Asclepius. Will you remember to pay the debt?’”
“The debt shall be paid,” replies Winter—meaning that resistance will continue.
On January 6-7, 2026, President Donald Trump flooded Minneapolis and St. Paul Minnesota with about 2,000 thuggish ICE agents.
During his 2024 campaign for President, Trump had promised—warned—that he would pursue “retribution” against those he believed had wronged him.
One of those was Minnesota Governor Tim Walz, who had dared to run against him as Kamala Harris’ vice presidential pick. Making Minnesota an even more attractive target for him was the state’s large Somali population, whom he had publicly labeled “garbage.”

ICE agents
Chad Davis, CC BY 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
But then the unexpected happened: Minnesota residents began a wholesale resistance to ICE efforts to arrest—and often brutalize—their immigrant friends and neighbors.
Minnesotans used whistles and encrypted chats to follow and document ICE activity. Starting in December, 2025, hundreds of people signed up for ICE observation training at a church in Uptown. Such trainings are now common.
The ICE killings of Renee Good and Alex Pretti steeled Minnesotans to turn out in even greater numbers to protest their occupiers. At great personal risk, motorists followed ICE agents’ vehicles and photographed their assaults on illegal aliens—and American citizens.
“In one city—in one city we have this outrage and this powder keg happening,” Deputy Attorney General Todd Blanche told Fox News. “And it’s not right. And it doesn’t happen anywhere else.”
Gregory Bovino, commanding “Operation Metro Surge,” noted: “They’ve got some excellent communications.”
In turn, Trump ordered Attorney General Pam Bondi to launch criminal investigations into Walz and Minneapolis Mayor Jacob Frey. They are accused of impeding federal immigration enforcement through public criticisms of ICE.
Trump-–like Adolf Hitler-–believes that power flows from the top down. He believes that if he “takes out” leaders like Walz and Frey, opposition to his rule will collapse.
He can’t understand—and cope with—a bottom-up movement driven by constituents, who—like the citizens in The Moon Is Down—have emboldened their leaders to stand their ground.
ABC NEWS, ADVICE, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BARACK OBAMA, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CNN, CORONAVIRUS, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOZ, DAVID BROOKS, DONALD TRUMP, DRUDGE RETORT, ECONOMY, EHRBERT HOOVER, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, FRANKLIN D. ROOSEVELT, GREAT DEPRESSION, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HARRY S. TRUMAN, MASKS, MEDIA MATTERS, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NBC NEWS, NEWSWEEK, NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI, NPR, NUEMBERG RALLIES, PBS NEWSHOUR, PENNSYLVANIA, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOCIAL DISTANCING, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE PBS NEWSHOUR, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWITTER, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UPI, USA TODAY, WISCONSIN, WONKETTE
In Bureaucracy, History, Politics, Social commentary on February 9, 2026 at 12:16 am
Voters who believed that Donald Trump cared about them should have asked themselves: “Does he care about my children?”
And the answer would have been: “No.”
The father of modern political science, Niccolo Machiavelli (1469 – 1527) is widely thought of as the personification of Satan.
Actually, Machiavelli was a passionate republican, who spent most of his life in the service of his beloved city-state, Florence.

Niccolo Machiavelli
In his masterwork, The Discourses, he warned that life is complex and no course of action is guaranteed safe or successful.
Donald Trump, on the other hand, is a man of simplistic “solutions” for simplistic audiences.
By early April, 2020, he had refused to issue a national “stay-at-home” order to contain the spread of the Coronavirus. When states began issuing shutdown orders of their own, he railed against those orders and demanded that “we need to reopen the country.”

Donald Trump
What lay behind this demand were two hidden agendas. He wanted to:
- Quickly revitalize—and take credit for—a once-booming economy, even though this was largely created by President Barack Obama.
- Return to his Nuremberg-style rallies, where he could slander anyone he wanted while basking in the worship of thousands of his fanatical followers.
Which is why he clearly missed this warning Machiavelli offered in The Discourses:
“…I shall speak here only of those dangers to which those expose themselves who counsel a republic or a prince to undertake some grave and important enterprise in such a manner as to take upon themselves all the responsibility of the same.
“For as men only judge of matters by the result, all the blame of failure is charged upon him who first advised it, while in case of success he receives commendations. But the reward never equals the punishment….
“I see no other course than to take things moderately, and not to undertake to advocate any enterprise with too much zeal, but to give one’s advice calmly and modestly.
“If either then the republic or the prince decides to follow it, they may do so, as it were, of their own will, and not as though they were drawn into it by your importunity.
“In adopting this course it is not reasonable to suppose that either the prince or republic will manifest any ill will towards you on account of a resolution not taken contrary to the wishes of the many.”
But, by May, 2020, more Americans were wary about “reopening the country” than about rushing to do so.
On the May 15, edition of The PBS Newshour, New York Times columnist David Brooks noted:
“If you look at actual behavior, people locked themselves down before any politician took a move. And even in those states where the politicians are opening up, people are still locking down….
“And so I think the key decisions right now are not being made in statehouses and certainly not the White House. They’re being made in living rooms, as people decide, is it safe? Can I go out?”
Coronavirus
By pushing his mantra—“America needs to reopen NOW!”—Trump was risking the lives of millions of Americans. But he was also risking the future of his Presidency.
If “reopening” the country proved disastrous, he had no back-up plan to offer.
Several states—such as Wisconsin and Pennsylvania—that re-opened saw swarms of people flooding into bars and restaurants. They didn’t wear masks or practice “social distancing.” Packed together like sardines, they offered themselves like a Right-wing sacrifice to Coronavirus.
The results were inevitable.
A new wave of COVID-19 erupted after America “reopened.” More employees were laid off—or refused to come to work for fear of Coronavirus.
The economy continued to tank.
As summer neared its end and millions of students faced returning to school, Trump offered his next “solution” to the Coronavirus pandemic: Send them back to school—-and not through virtual classes at home.
Trump wanted children to return to possibly COVID-19-infected classrooms.
And he wasn’t asking parents to send their children back to school. He was ordering them to.
On July 8, 2020, he tweeted that he might withhold federal funding from schools that did not resume in-person classes that fall.
Why was he so insistent on this?
Trump knew that before parents could return to work, their kids needed to return to class, He hoped that would boost the economy—for which he could take credit.
And that would boost his chances for re-election in November.
Just as the ancient Canaanites sacrificed their children to the god Moloch, so Trump expected his followers—and opponents—to risk their children’s lives for him.


Ancient Canaanites offering their children as sacrifices to Moloch
And the sacrifices quickly started coming. Approximately 2.1 million children in the United States tested positive for COVID-19 by the end of December 2020.
Those who supported Trump in 2020 clearly valued the lives of their children far less than putting a ruthless psychopath back into power.
And, in 2024, 77 million Americans forgave him the loss—or near-loss—of their children and sent him back to the White House.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2024 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ABUSE OF POWER, ADOLF HITLER, AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AILEEN CANNON, AIR TRAFFIC CONTROLLERS, AIR TRAFFICK CONTROLLERS, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, AUSTRIA, AXIOS, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BERLIN, BIRD FLU, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BORDER WALL, BRIAN KEMP, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION (CDC) CHINA, CHINA, CIA, CLASSIFIED DOCUMENTS, CLAUS VON STAUFFENBERG, CLIMATE CHANGE, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DAILY KOS, DANIEL CASSINO, DAVID BROOKS, DEMOCRACY, DEMOCRATS, DIVERSITY, DIVERSITY EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI) PROGRAMS, DONALD TRUMP, ELECTORAL COLLEGE, EMILY MURPHY, ENGLAND, EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI), FBI, FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION (FAA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT ADMINISTRATION (FEMA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, FRANCE, FRATERNAL ORDER OF POLICE, FUEL PRICES, GAIUS CALIGULA, GALLUP POLL, GAZA, GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION, GEORGE FLOYD, GLOBAL CONFLICT, GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, GROCERY PRICES, GULF OF MEXICO, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HILLARY CLINTON, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, HUNTER BIDEN, illegal immigration, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), IMPEACHMENT, INFLATION, INSPECTORS GENERAL, INSURRECTION ACT, INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CHIEFS OF POLICE, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, ISRAEL, JACK SMITH, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JARED KUSHNER, JEFF SESSIONS, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN ADAMS, JOHN F. KENNEDY CENTER FOR THE PERFORMING ARTS, JONATHAN ROSS, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPH STALIN, JUAN ORLANDO HERNANDEZ, Kamala Harris, KEVIN MCCARTHY, KIM JONG-UN, LAMAR ALEXANDER, LATINOS, LETITIA JAMES, MACHISMO, MAR-A-LAGO, MARJORIE TAYLOR GREENE, MARK MEADOWS, MARTIN GUGINO, MASCULINITY, MEASLES, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICAID, MEDICARE, MERRICK GARLAND, MIKE PENCE, MISOGYNY, MITCH MCCONNELL, MOHAMMED BIN SALMAN, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUNICH CONFERENCE, MUSLIMS, NANCY PELOSI, NATIONAL GUARD, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY (NSA), NAVAHO CODE TALKERS, NAVAJO COLDE TALKERS, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NIHILISM, NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION (NATO), NORTH KOREA, NORTH KORREA, NPR, OBSTRUCTION OF CONGRESS, PARDONS, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLAND, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAFAEL EDUARDO "TED" CRUZ, RAW STORY, RENEE NICOLE GOOD, REPUBLICAN PARTY, REPUBLICANS, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, ROBERT F. KENNEDY JR., RODNEY KING, ROME, RON JOHNSON, RUDY GIULIANI, RUSSIA, SALON, SAUDI ARABIA, SEATTLE TIMES, Secret Service, SERGEY KISLYAK, SERGEY LAVROV, SLATE, SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRITION ASSISTANCE PROGRAM (SNAP), TALKING POINTS MEMO, TERRORISM, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE RISE AND FALL OF THE THIRD REICH (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WALL STREET JOURNAL, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, THIRD REICH, THOMAS MATTHEW CROOKS, TIM WALZ, TIME, TRANSPORTATION COSTS, TREASON, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEEE AIRMEN, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWENTY-FIFTH AMENDMENT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, TY COBB, U.S. BORDER PATROL, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UKRAINE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE (DOD), UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE (DOJ), UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UNITED STATES SENATE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, VOLODMYR ZELENSKY, VOTER SUPPRESSION, VOX, WILLIAM L. SHIRER, WOMEN, WONKETTE, WORLD WAR 11, X, XI JINPING
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on February 6, 2026 at 12:58 am
Of all the threats that President Donald Trump poses to American democracy, none may be more deadly than his repeated threats to invoke the Insurrection Act.
This is an 1807 law that empowers the President to deploy the Armed Forces to individual states in specific circumstances, such as the suppression of civil disorder, insurrection, and armed rebellion against the federal government.
What is arousing Trump’s fury is the civil unrest he’s ignited in Minneapolis, Minnesota—especially following the January 7 shooting of Renee Nicole Good, a 37-year-old writer and poet, by Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agent Jonathan Ross.

Renee Good
He’s ordered the Justice Department to criminally investigate Minnesota Governor Tim Walz and Minneapolis Mayor Jacob Frey for allegedly conspiring to impede federal immigration agents.
Their “crime”: Daring to criticize the aggressive behavior of thousands of ICE and Border Patrol agents deployed in Minnesota.
Walz said in a statement: “Weaponizing the justice system and threatening political opponents is a dangerous, authoritarian tactic. The only person not being investigated for the shooting of Renee Good is the federal agent who shot her.”
“This is an obvious attempt to intimidate me for standing up for Minneapolis, our local law enforcement, and our residents against the chaos and danger this Administration has brought to our streets,” Frey said in a statement to CBS News.
“I will not be intimidated. My focus will remain where it’s always been: keeping our city safe.”

Jacob Frey
Czbik, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Attorney Ty Cobb—who served as a White House lawyer in the first Trump Administration but is now a scathing critic of the president—warns that the tensions in Minneapolis could go from bad to worse if Trump invokes the Insurrection Act.
“During the first Trump administration, there were guardrails back then. There were people who could say ‘no’ to the president. And now, he’s surrounded by sycophants and enablers and people who don’t say no.
“I mean, it’s just stunning the number of people that have signed on for what’s going on in Minnesota and what’s going on in Greenland—you know, things that would have never been tolerated in the first 250 years of our democracy.

Ty Cobb
John Mathew Smith & http://www.celebrity-photos.com from Laurel Maryland, USA, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
“But I do think he wants—desperately wants—to invoke the Insurrection Act….I think martial law is definitely in the cards. And it’s a way that he’ll be able to control the elections.”
* * * * *
Countless historians have tried to answer the question: “Was the rise of Adolf Hitler—and the catastrophe he unleashed—inevitable?”
William L. Shirer, author of the monumental The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich, apportioned German guilt as follows:
“The cardinal error of the Germans who opposed Nazism was their failure to unite against it. At the crest of their popular strength, in July 1932, the National Socialists had attained but 37 percent of the vote. But the 63 percent of [Germans] who expressed their opposition to Hitler were much too divided and shortsighted to combine against a common danger which they must have known would overwhelm them unless they united, however temporarily, to stamp it out.”
Competent future historians may reach the same conclusion about American voters in 2024.
- Republicans: Who feared that Trump’s Fascistic supporters would deprive them of political office if they didn’t abase themselves to a lifelong criminal and would-be dictator.
- Republican judges: Who bent and/or broke the law to enable Trump to escape justice.
- Justice Department prosecutors: Whose awe of the Presidency allowed Trump to slander and threaten federal prosecutors and judges.
- Attorney General Merrick Garland: Whose cowardice prevented him from appointing Jack Smith Special Counsel until November 18, 2022—giving Trump time to delay justice and again win the Presidency.
- Democrats: Whose cowardice toward Trump encouraged Republicans to ever more extreme measures.
- Police officers: The International Association of Chiefs of Police and the Fraternal Order of Police issued a joint statement condemning clemency for criminals who assault law enforcement officers—but did not explicitly indict the January 6 actions. The Fraternal Order of Police endorsed Donald Trump in 2024.
- History illiterate voters: Who were eager to scrap alliances—such as NATO—that had checked Soviet aggression since the end of World War II.
- Nihilists: With nothing positive to contribute, their attitude was to destroy American institutions that had created prosperity and security for decades.
- Blacks: Voted for a racist in hopes of a bigger paycheck.
- Muslims: Refused to vote for Kamala Harris because Joe Biden wouldn’t stop Israel’s military campaign to free Hamas-captured hostages.
- Hispanics: Like the Jews in Hitler’s Germany, who couldn’t believe that Trump would carry out his threats to imprison and/or deport them.
- The Biden administration: Which refused to stem the tide of illegal aliens invading America—and thus enraged millions of law-abiding Americans into supporting Trump.
- Toxic masculinity voters: Whose misogynistic attitudes toward women led them to reject a former local and state prosecutor for a 34-times convicted felon.
- American voters: Whose hatred of Hispanic illegal aliens and inflationary grocery prices led them to ignore overwhelming evidence of Trump’s intent to overturn the democratic process and make himself absolute dictator.
In short: Those opposed to Donald Trump’s evil were too divided and shortsighted to combine against a common danger.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2024 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ABUSE OF POWER, ADOLF HITLER, AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AILEEN CANNON, AIR TRAFFIC CONTROLLERS, AIR TRAFFICK CONTROLLERS, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, AUSTRIA, AXIOS, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BERLIN, BIRD FLU, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BORDER WALL, BRIAN KEMP, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION (CDC) CHINA, CHINA, CIA, CLASSIFIED DOCUMENTS, CLAUS VON STAUFFENBERG, CLIMATE CHANGE, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DAILY KOS, DANIEL CASSINO, DAVID BROOKS, DEMOCRACY, DEMOCRATS, DIVERSITY, DIVERSITY EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI) PROGRAMS, DONALD TRUMP, ELECTORAL COLLEGE, EMILY MURPHY, ENGLAND, EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI), FBI, FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION (FAA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT ADMINISTRATION (FEMA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, FRANCE, FRATERNAL ORDER OF POLICE, FUEL PRICES, GAIUS CALIGULA, GALLUP POLL, GAZA, GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION, GEORGE FLOYD, GLOBAL CONFLICT, GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, GROCERY PRICES, GULF OF MEXICO, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HILLARY CLINTON, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, HUNTER BIDEN, illegal immigration, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), IMPEACHMENT, INFLATION, INSPECTORS GENERAL, INSURRECTION ACT, INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CHIEFS OF POLICE, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, ISRAEL, JACK SMITH, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JARED KUSHNER, JEFF SESSIONS, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN ADAMS, JOHN F. KENNEDY CENTER FOR THE PERFORMING ARTS, JONATHAN ROSS, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPH STALIN, JUAN ORLANDO HERNANDEZ, Kamala Harris, KEVIN MCCARTHY, KIM JONG-UN, LAMAR ALEXANDER, LATINOS, LETITIA JAMES, MACHISMO, MAR-A-LAGO, MARJORIE TAYLOR GREENE, MARK MEADOWS, MARTIN GUGINO, MASCULINITY, MEASLES, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICAID, MEDICARE, MERRICK GARLAND, MIKE PENCE, MISOGYNY, MITCH MCCONNELL, MOHAMMED BIN SALMAN, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUNICH CONFERENCE, MUSLIMS, NANCY PELOSI, NATIONAL GUARD, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY (NSA), NAVAHO CODE TALKERS, NAVAJO COLDE TALKERS, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NIHILISM, NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION (NATO), NORTH KOREA, NORTH KORREA, NPR, OBSTRUCTION OF CONGRESS, PARDONS, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLAND, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAFAEL EDUARDO "TED" CRUZ, RAW STORY, RENEE NICOLE GOOD, REPUBLICAN PARTY, REPUBLICANS, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, ROBERT F. KENNEDY JR., RODNEY KING, ROME, RON JOHNSON, RUDY GIULIANI, RUSSIA, SALON, SAUDI ARABIA, SEATTLE TIMES, Secret Service, SERGEY KISLYAK, SERGEY LAVROV, SLATE, SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRITION ASSISTANCE PROGRAM (SNAP), TALKING POINTS MEMO, TERRORISM, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE RISE AND FALL OF THE THIRD REICH (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WALL STREET JOURNAL, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, THIRD REICH, THOMAS MATTHEW CROOKS, TIM WALZ, TIME, TRANSPORTATION COSTS, TREASON, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEEE AIRMEN, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWENTY-FIFTH AMENDMENT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, TY COBB, U.S. BORDER PATROL, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UKRAINE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE (DOD), UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE (DOJ), UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UNITED STATES SENATE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, VOLODMYR ZELENSKY, VOTER SUPPRESSION, VOX, WILLIAM L. SHIRER, WOMEN, WONKETTE, WORLD WAR 11, X, XI JINPING
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on February 5, 2026 at 12:10 am
In 2024, nihilism—and its adherents—played a key role in reelecting Donald Trump President of the United States.
During the 2024 Presidential campaign Trump promised to appoint Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., as Secretary of Health and Human Services.
On October 27, 2024, Trump told a rally in Madison Square Garden: “I’m going to let him go wild on health. I’m going to let him go wild on the food. I’m going to let him go wild on the medicines.”
Kennedy, the son of the late Senator Robert F. Kennedy, is a self-admitted former 14-year heroin addict, which he has said began at age 15. In a 2012 deposition he claimed that doctors found a dead parasitic worm in his brain, which he believed caused significant memory loss and brain fog around 2010.

Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.
Since 2005, Kennedy has peddled vaccine misinformation and public health conspiracy theories. Among these:
- Vaccines cause autism.
- The COVID-19 vaccine—which has saved countless lives—is “the deadliest vaccine ever made.”
- There is no comprehensive system for monitoring vaccine safety.
Since Kennedy took office on February 13, 2025:
- February 14, 2025: Around 1,300 employees of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) were laid off by the administration, including all first-year officers of the Epidemic Intelligence Service.
- August: Over 600 CDC employees were laid off. Among programs completely dismantled: Maternal and child health services, oral health, and the Violence Against Children and Youth Surveys.
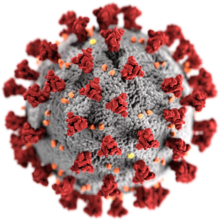
- By July 7, 2025, 1,281 measles cases had been reported, more than the 1,274 measles cases reported in all of 2019. This was the highest level of cases since the disease had been declared eliminated in 2000.
- Roughly 93% of infections in 2025 and 95% so far in January, 2026, were among unvaccinated people or those with an unknown vaccination status. And this can be directly traced to the influence of anti-vaccine conspiracy-spreaders like Kennedy.

Measles virus
Since becoming President again on January 20, 2025, Donald J. Trump has aggressively committed a series of outrages against his fellow Americans, including:
- Granting clemency to more than 1,500 people convicted of offenses related to the January 6, 2021 United States Capitol attack.
- Signing 26 executive orders reversing climate change initiatives, eliminating DEI programs, changing the federal designation for the Gulf of Mexico to the “Gulf of America” and initiating a federal hiring freeze.
- Revoking an executive order on Artificial Intelligence safety signed by former President Joseph Biden, to establish safeguards for the rapidly advancing AI technology.
- Firing the inspectors general—who are charged with protecting the government from waste and corruption—from more than a dozen federal agencies.
- Purging about a half-dozen executive assistant directors at the FBI. These were some of the bureau’s top managers overseeing criminal, national security and cyber investigations. Their “crime”: Investigating Trump’s inciting the January 6, 2021 coup attempt and illegally holding highly sensitive national security documents after leaving office.
- Following Trump’s anti-DEI executive order, the Department of Defense deleted content that included the achievements of nonwhites—such as Navajo code talkers, black Tuskegee Airmen, Medal of Honor winners and women veterans.
- Firing the board members at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts and appointing himself as chairman—just as Joseph Stalin made himself arbiter of what was permissible for artists in the Soviet Union.
- Ordering the Justice Department to indict his critics such as New York Attorney General Letitia James and former FBI Director James Comey.
- James had convicted him on 34 felony counts of falsifying business records. Comey had sought to investigate Russia’s subversion of the 2016 Presidential campaign to ensure Trump’s election.
- Shutting down the Federal Government on October 1, when Democrats refused to agree to his gutting Medicaid, Medicare and the Affordable Care Act (ACA), causing 10-15 million Americans to lose health insurance coverage.
- Among those not getting paid: Air traffic controllers for the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). Owing to many controllers refusing to work, the FAA reduced air traffic by 10% at many airports.
- Shutting off the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) for the poor to pressure Democrats to support his gutting of healthcare programs.
- Flooding the streets of Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., Chicago with federalized National Guard troops against state governors’ wishes during immigration crackdowns and civil unrest.
- Flooding Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota, with 3,000 Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents who are terrorizing (and in one case murdering) both American citizens and illegal aliens.
- Governors have requested the deployment of federal troops—such as in Arkansas in 1957 for school desegregation and in California in 1992 during the Los Angeles riots following the Rodney King verdict. But Trump is the first President to deploy troops against the wishes of states’ governors.
- Pardoning favored political allies and loyalists. Among these: Seventy-seven people associated with the Trump fake electors plot to overturn the results of the 2020 U.S. presidential election, including Trump’s personal attorney Rudy Giuliani and former chief of staff Mark Meadows.
- Others included: Former Honduras president Juan Orlando Hernández, sentenced to 45 years’ imprisonment for moving tons of cocaine to the United States.
- Threatening to invade Greenland, a self-governing, autonomous part of the Kingdom of Denmark. The United States has recognized Denmark’s ties to Greenland since 1917 and signed a joint defense agreement in 1951.
- As Denmark is a member of NATO, an attack on Greenland would ignite a war between the United States and its NATO allies.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2024 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ABUSE OF POWER, ADOLF HITLER, AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AILEEN CANNON, AIR TRAFFIC CONTROLLERS, AIR TRAFFICK CONTROLLERS, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, AUSTRIA, AXIOS, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BERLIN, BIRD FLU, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BORDER WALL, BRIAN KEMP, BUZZFEED, CBS NEWS, CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION (CDC) CHINA, CHINA, CIA, CLASSIFIED DOCUMENTS, CLAUS VON STAUFFENBERG, CLIMATE CHANGE, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DAILY KOS, DANIEL CASSINO, DAVID BROOKS, DEMOCRACY, DEMOCRATS, DIVERSITY, DIVERSITY EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI) PROGRAMS, DONALD TRUMP, ELECTORAL COLLEGE, EMILY MURPHY, ENGLAND, EQUITY AND INCLUSION (DEI), FBI, FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION (FAA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT ADMINISTRATION (FEMA), FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, FRANCE, FRATERNAL ORDER OF POLICE, FUEL PRICES, GAIUS CALIGULA, GALLUP POLL, GAZA, GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION, GEORGE FLOYD, GLOBAL CONFLICT, GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, GROCERY PRICES, GULF OF MEXICO, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HILLARY CLINTON, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, HUNTER BIDEN, illegal immigration, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), IMPEACHMENT, INFLATION, INSPECTORS GENERAL, INSURRECTION ACT, INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CHIEFS OF POLICE, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, ISRAEL, JACK SMITH, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JARED KUSHNER, JEFF SESSIONS, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN ADAMS, JOHN F. KENNEDY CENTER FOR THE PERFORMING ARTS, JONATHAN ROSS, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPH STALIN, JUAN ORLANDO HERNANDEZ, Kamala Harris, KEVIN MCCARTHY, KIM JONG-UN, LAMAR ALEXANDER, LATINOS, LETITIA JAMES, MACHISMO, MAR-A-LAGO, MARJORIE TAYLOR GREENE, MARK MEADOWS, MARTIN GUGINO, MASCULINITY, MEASLES, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICAID, MEDICARE, MERRICK GARLAND, MIKE PENCE, MISOGYNY, MITCH MCCONNELL, MOHAMMED BIN SALMAN, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUNICH CONFERENCE, MUSLIMS, NANCY PELOSI, NATIONAL GUARD, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY (NSA), NAVAHO CODE TALKERS, NAVAJO COLDE TALKERS, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NIHILISM, NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION (NATO), NORTH KOREA, NORTH KORREA, NPR, OBSTRUCTION OF CONGRESS, PARDONS, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLAND, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RAFAEL EDUARDO "TED" CRUZ, RAW STORY, RENEE NICOLE GOOD, REPUBLICAN PARTY, REPUBLICANS, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, ROBERT F. KENNEDY JR., RODNEY KING, ROME, RON JOHNSON, RUDY GIULIANI, RUSSIA, SALON, SAUDI ARABIA, SEATTLE TIMES, Secret Service, SERGEY KISLYAK, SERGEY LAVROV, SLATE, SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRITION ASSISTANCE PROGRAM (SNAP), TALKING POINTS MEMO, TERRORISM, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE RISE AND FALL OF THE THIRD REICH (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WALL STREET JOURNAL, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, THIRD REICH, THOMAS MATTHEW CROOKS, TIM WALZ, TIME, TRANSPORTATION COSTS, TREASON, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEEE AIRMEN, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWENTY-FIFTH AMENDMENT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, TY COBB, U.S. BORDER PATROL, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UKRAINE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE (DOD), UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE (DOJ), UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UNITED STATES SENATE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, VOLODMYR ZELENSKY, VOTER SUPPRESSION, VOX, WILLIAM L. SHIRER, WOMEN, WONKETTE, WORLD WAR 11, X, XI JINPING
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Medical, Politics, Social commentary on February 4, 2026 at 12:10 am
Throughout 2024, Democrats expected to receive support from their traditional allies—such as blacks and Hispanics. But that didn’t happen.
During the eight-year tenure of Barack Obama, America’s first black President, Donald Trump attacked him as a foreign-born citizen who was thus ineligible for that office.
Trump also had a history of supporting—and being supported by—racist white groups like the Proud Boys and the Oath Keepers.
Nevertheless, blacks deserted Vice President Kamala Harris in droves. About three in 10 back men under age 45 went for Trump, roughly double the share he got in 2020. A clear majority of young black voters described the economy as “not so good” or “poor,” compared with about half of older black voters.

Despite Trump’s demands for “mass deportations,” numerous Hispanics, when interviewed, said they didn’t feel threatened. They felt certain that Trump would deport “only the bad people.”
Young Latinos, particularly young Latino men, were more supportive of Trump than in 2020. Roughly half of young Latino men voted for Harris, compared with about six in 10 who went for Trump.
Majorities of black and Latino voters said the economy was in bad shape. They wanted a bigger paycheck. And they were willing to re-elect a man who despised them in hopes of getting it.
Muslims—especially those living in Dearborn, Michigan—made their own contribution to Trump’s re-election: They played a losing blackmail game with the Biden administration.
On October 7, 2023, under the cover of thousands of rockets fired from Gaza, Hamas terrorists slaughtered an estimated 1,139 men, women and children in Israeli streets, houses, kibbutz communities and at a rave music festival.
About 250 others were kidnapped and taken into Gaza. Israel responded by declaring a state of war—pounding Gaza with bombs, missiles. tanks and soldiers.

Palestinians celebrating the attack on Israel
Terrorism-sympathizing Islamics—especially in Michigan—demanded that the Biden administration stop sending military equipment to Israel—and force Israelis to stop their military campaign to free the hostages. They threatened: “If you don’t do what we want, we won’t vote for Kamala Harris.”
Biden and Harris rejected their demands—and Islamics voted for Trump or didn’t vote at all.
The result: A reelected Trump launched an aggressive campaign to restrict immigration from Islamic nations and deport Islamic immigrants accused of sympathizing with Hamas.
Ignorance of and/or contempt for history played a major role in reelecting Trump.
“Low information voters” is a euphemism for people dangerously ignorant of and/or indifferent to the issues affecting their lives.
After World War II ended in 1945, the United States proved a force for worldwide stability. Its “nuclear umbrella” prevented a Russian takeover of Europe and a Chinese takeover of Asia.
But voters ignored Trump’s “bromance” with Communist dictators Vladimir Putin (Russia), Xi Jinping (China) and Kim Jong-Un (North Korea). They also ignored his proven disdain for the leaders of democratic nations—such as Canada and Great Britain.

A strong isolationist sentiment motivated many of these voters—the belief that the United States didn’t need alliances with other nations, especially European ones. They ignored—or were ignorant of—that the defeat of Nazi Germany had required the unlikely alliance of the United States, Great Britain and the Soviet Union.
Also ignored—deliberately or through ignorance—the vital role the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) had played since World War II in maintaining peace throughout Europe—and deterring the Soviet Union from aggression.
Many Right-wing voters believe that the United States had been too active in international affairs since the end of World War II and had gotten little or nothing in return.
Nihilists made their own significant contribution to Trump’s return to power.
On August 21, 2025, conservative New York Times columnist David Brooks outlined the fundamental change that had occurred in conservatism since 1983:
“When I was emerging from college, we conservatives thought we were conserving something — a group of cultural, intellectual and political traditions — from the postmodern assault.
“But decades later, with the postmodern takeover fully institutionalized, [Right-wingers] don’t seem to think there’s anything to conserve. They are radical deconstructors….This is a key difference between old-style conservatism and Trumpism.
“But there’s another, even more radical reaction to [liberalism]: nihilism. You start with the premise that progressive ideas are false and then conclude that all ideas are false.
“Faith in God has been on the decline for decades; so has social trust, faith in one another; so has faith in a dependable career path. A recent Gallup poll showed that faith in major American institutions is now near its lowest point in the 46 years Gallup has been measuring these things. But the core of nihilism is even more acidic; it is the loss of faith in the values your culture tells you to believe in.”
Nothing better illustrated this nihilistic streak—and Trump’s willingness to play to it—than his promise, during the 2024 Presidential campaign, that he planned to decimate the American healthcare system: His Secretary of Health and Human Services would be Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.










AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA), AFGHANISTAN, ALEX PRETTI, ALLEN DULLES, ALTERNET, AMAZON, AMERICABLOG, ANTI-CASTRO CUBANS, AP, APPLE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, ASSASSINATION, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BARACK OBAMA, BARI WEISS, BAY OF PIGS, BBC, BIG TECH, BLACKS, BLOOMBERG, BLUESKY, BUZZFEED, CANADA, CANADIANS, CARLOS MARCELLO, CBS NEWS, CIA, CITIENSHIP TESTS, CIVIL RIGHTS, CLEAR AND PRESENT DANGER (FILM), CNN, COLUMBIAN/MEXICAN DRUG CARTELS, CONSPIRACIES, CROOKS AND LIARS, CUBA, CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS, CUSTOMS AND BORDER PATROL (CBP), DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, FBI, FBI AGENTS, FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY, FEDERAL RESERVE, FEDERAL TRADE COMMISSION, FIDEL CASTRO, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAZA, GOOGLE, GREENLAND, GREENLANDERS, GUN RIGHTS ENTHUSIASTS, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HARRISON FORD, HISPANICS, HUFFINGTON POST, IMMIGRANTS, IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT (ICE), INSPECTORS GENERAL, INTERNATIONAL BROTHERHOOD OF TEAMSTERS, IRAN, IRANIANS, ISLAM, ISRAEL, ISREAL, J. EDGAR HOOVER, JAIME DIMON, JAMES COMEY, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JEFF BEZOS, JEFFREY, JEFFREY EPSTEIN, JEROME POWELL, JIMMY HOFFA, JOE BIDEN, JOHN F. KENNEDY, JOHN KELLY, JOURNALISTS, JP MORGAN CHASE, JUSTICE DEPARTMENT PROSECUTORS, Kamala Harris, KGB, LAWYERS, LEBANON, LETITIA JAMES, MAFIA, MARCUS AURELIUS, MARINE BARRACKS BOMBING, MARK ESPER, MARK MILLEY, MEDAL OF HONOR WINNERS, MEDIA MATTERS, MEDICARE, MELANIA TRUMP, META, MICHELLE OBAMA, Military, MINNESOTA, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, MUSLIMS, NATIONAL RIFLE ASSOCIATION (NRA), NATO, NAVAJO CODE TALKERS, NBC NEWS, NERO, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, NUCLEAR REACTOR SITES, NUCLEAR TEST BAN TREATY, NUCLELAR TEST BAN TREATY, OIL MILLIONAIRES, PAKISTAN, PAM BONDI, PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, PBS NEWSHOUR, PETE HEGSETH, POLICE, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, RARE EARTH MIINERALS, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROBERT F. KENNEDY, Ronald Reagan, RUDY GIULIANI, SALON, SAM GIANCANA, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOMALIS, SOUTHERN RACISTS, SOVIET UNION, SUICIDE BOMBINGS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, TARIFFS, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE KENNEDY HALF-CENTURY (BOOK), THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE MILITARY, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE PRESS, THE PRINCE (BOOK), THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIM COOK, TIME, TRAJAN, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TUSKEGEE AIRMEN, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE, UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, WATERGATE, X
JFK HAD POWERFUL ENEMIES. SO DOES DJT: PART TWO (OF FOUR)
In Bureaucracy, Business, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Medical, Military, Politics, Social commentary on February 17, 2026 at 12:12 amJust as President John F. Kennedy was passionately loved and hated, so, too, is Donald J. Trump. And Trump, at 79, has already been the target of two assassination attempts.
Donald Trump
Among the reasons why Trump is so widely hated:
Alex Pretti
Greenland
Columbian drug lords
Share this: