Posts Tagged ‘EAST GERMANY’
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ERNEST BORGNINE, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, Robert Ryan, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THE WILD BUNCH (MOVIE), THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WILLIAM HOLDEN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on October 31, 2025 at 12:10 am
On July 20, 1944, Colonel Claus Schenk von Stuaffenberg tried to assassinate Nazi Germany’s Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, with a time bomb.
Stauffenberg appeared at Hitler’s well-guarded military headquarters in East Prussia. Like all his other outposts, Hitler had named it—appropriately enough—“Wolf’s Lair.”
While a war conference was in session, he placed his yellow briefcase next to Hitler—who was standing with his generals at a heavy oaken table. Then he excused himself to take an “urgent” phone call.

“Wolf’s Lair”
But after Stauffenberg left the room, Colonel Heinz Brandt, who stood next to Hitler, found the briefcase blocking his legs. So he moved it—to the other side of the heavy oaken support, thus unknowingly shielding Hitler from the full blast.
At 12:42 p.m. on July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg’s briefcase bomb erupted.
Brandt died, as did two other officers and a stenographer. Hitler not only survived, but the plotters failed to seize the key broadcast facilities of the Reich.
This allowed Hitler to make a late-night speech to the nation, revealing the failed plot and assuring Germans that he was still alive. And he swore to flush out the “traitorous swine” who had tried to kill him.
Mass arrests quickly followed. Among the first victims discovered and executed was the conspiracy’s leader, Colonel Claus von Stauffenberg. Standing before a makeshift firing squad at midnight, he cried: “Long live our sacred Germany!”

Claus von Stauffenberg
At least 7,000 persons were arrested by the Gestapo. Of these, 4,980 were executed.
If the conspiracy had succeeded and Germany had surrendered in July or August, 1944, World War II would have ended eight to nine months earlier. This would have meant:
- The Russians—who didn’t reach Germany until April, 1945—could not have occupied the Eastern part of the country.
- Millions of East Germans would have been spared the misery of living under Communist rule for 44 years.
- Many of the future conflicts between the United States and the Soviet Union over access to West Berlin and/or West Germany would have been prevented.
- Untold numbers of Holocaust victims would have survived because the concentration camps would have been shut down far earlier.
Yet history notes other tyrants whose evil reigns ended prematurely—such as that of Gaius Caligula.
Caligula became Emperor of Rome in 37 A.D. after succeeding the Emperor Tiberius, his uncle.
For three years, he held—and exercised—life-or-death power over the citizens of Italy and beyond. His attitude toward humanity was best summed up by his remark: “Bear in mind that I can treat anyone exactly as I please.”

Gaius Caligula
Carole Raddato from FRANKFURT, Germany, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Among his litany of crimes, according to his biographer, Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus:
- He forced parents to attend the executions of their sons, sending a litter for one man who pleaded ill health. He invited another to dinner immediately after witnessing the execution, and trying to rouse him to gaiety by a great show of affability.
- He watched for several successive days as the manager of his gladiatorial shows was beaten with chains, and ordered him killed only when he was disgusted at the stench of his putrefied brain.
- He appeared at the temple of Castor and Pollux to be worshiped as Jupiter Latiaris.
- He lived in incest with all his three sisters. At a large banquet he placed each of them in turn below him, while his wife reclined above.
- He intended to promote his favorite racehorse, Incitatus (“Swift”), to consul.
Like all Roman emperors, Caligula was constantly protected by the Praetorian Guard, an elite unit of the Roman army comprised of tough legionnaires—especially German ones.
There had not been an assassination of a Roman emperor since the death of Julius Caesar almost 100 years earlier.
The assassins in that case had been motivated by a mixture of
- Personal animosity toward Caesar’s increasing arrogance and
- Genuine fears that he intended to abolish the Roman Republic and set himself up as a dictator.
And Caligula intended to keep a similar fate from overtaking him.
For all his cruelty and egomania, the trait that finally destroyed Caligula was his joy in humiliating others.
Among those he taunted was Cassius Chaerea, a member of his own bodyguard.
Two different historians give two different motives for his decision to assassinate Caligula.
The Jewish historian Josephus claimed that Chaerea was a “noble idealist” deeply committed to “Republican liberties.”
But Suetonius wrote that Caligula considered Chaerea effeminate because of a weak voice and gave him such mocking watchwords as “Priapus” and “Venus.” Whenever Caligula had Chaerea kiss his ring, the emperor would “hold out his hand to kiss, forming and moving it in an obscene fashion.”
On January 22 41 A.D. Chaerea and several other bodyguards hacked Caligula to death with swords before other guards could save him.
The assassination attempts on Adolf Hitler and the successful assassination of Gaius Caligula demonstrate that the greatest danger facing a tyrant is people who:
- Are in frequent and highly personal contact with him; and
- Keep their animosity toward him a secret—until the moment they wish to strike.
Had Secret Service agent Kerry O’Grady kept her revulsion toward Donald Trump to herself, she might now be hailed as an American traitor—or as democracy’s savior.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ERNEST BORGNINE, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, Robert Ryan, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THE WILD BUNCH (MOVIE), THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WILLIAM HOLDEN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on October 30, 2025 at 12:10 am
Where does loyalty leave off and conscience begin?
Specifically: If you’re a bodyguard for a man you know represents a genuine threat to democracy, what are your obligations to defend him? Should you be as willing to “take a bullet” for him as for someone you truly admire?
Members of Adolf Hitler’s bodyguard faced no such qualms. Right up to the bitter end, with Russian forces only blocks from the Fuhrerbunker, they manned their posts, ready to die for the man who had led them—and Germany—into the ultimate catastrophe.
They made Hitler a closely-guarded target.
He was surrounded by fanatical bodyguards who were expert marksmen. He often wore a bulletproof vest and a cap lined with three pounds of laminated steel.
But his single greatest protection—he claimed—was an instinct for danger. He would suddenly change his schedule—to drop in where he was least expected. Or suddenly depart an event where he was expected to stay a long time.

Adolf Hitler
It wasn’t Hitler’s bodyguards who posed a threat to his life. It was the colonels and generals of the German General Staff.
On August 20, 1934, members of the German army, navy and air force were required to swear the “Law On The Allegiance of Civil Servants and Soldiers of the Armed Forces.”
Whereas members of the armed forces had previously sworn loyalty to Germany, the new law required them to swear an oath of loyalty to Hitler personally.
In coming years, this would prove a deadly trap for many German officers—forcing them to choose between betraying a sacred oath and remaining loyal to a man who was clearly driving Germany to ruin.
For those officers who could not abide Germany’s coming destruction, the choice was simple: Hitler had to go.
A series of assassination attempts were made against Hitler. All of them involved time-bombs. And all of the would-be assassins were members of the German General Staff.
In one case, a bomb secretly stashed aboard Hitler’s plane failed to explode. In another, an officer who had a bomb strapped to himself unexpectedly found his scheduled meeting with Hitler called off. He had to rush into a bathroom to defuse the bomb before it exploded.
Hitler came closest to death on July 20, 1944.
Colonel Claus Schenk von Stuaffenberg was the driving force in a plot to assassinate Hitler with a time bomb.

Claus von Stauffenberg
He had served with the Wehrmacht in Poland (1939), France (1940) and the Soviet Union (1941). While serving in Tunisa, he was seriously wounded on April 7, 1943, when Allied fighters strafed his vehicle. He lost his left eye, right hand and two fingers of his left hand after surgery.
For most of his fellow officers, the motive was craven: The “happy time” of German victories was over. Germany was losing the war it had unleashed on the world in 1939—and now they feared the worst.
This was especially true now that the numerically superior forces of the Soviet Union had gone onto the offensive.

The Wehrmacht in Russia
The Wehrmacht and Schutzstaffel (SS) had killed millions of Russians. Many had died in combat. Others had been murdered as captives. Still more had been allowed to die by starvation and exposure to the notorious Russian winter.
For Stauffenberg, there was another reason: His disgust at the horrors he had seen committed by his fellow Wehrmacht soldiers upon defenseless POW’s and civilians in Russia.
Thus, Stauffenberg—more than many Germans—knew firsthand the vengeance his country could expect if the “Thousand-Year Reich” fell. Something must be done, he believed, to prove to the world that not all Germans—even members of the Wehrmacht—were criminals.
Most of the conspirators wanted to arrest Hitler and surrender to British and American forces—well before the much-feared Russians gained a toehold in Germany. Stauffenberg didn’t want to arrest Hitler; he wanted to kill him. A live Hitler might eventually be rescued by his Nazi colleagues.
Stauffenberg intended to carry his bomb—hidden in a briefcase—into a “Hitler conference” room packed with military officers. Rigged with a time-fuse, it would be left there while he found an excuse to leave. After the explosion, he would phone one of his fellow conspirators with the news.
Stauffenberg intended to direct the new government that would replace that of the Nazis—and open peace talks with the British and Americans. With Hitler dead, the coup—“Operation Valkyrie”—would be on.
Anti-Nazi conspirators would seize control of key posts of the government. They would inform the British and Americans of Germany’s willingness to surrender. Provided, of course, that the vengeance-seeking Russians did not have a say in its postwar future.
On July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg appeared at Hitler’s well-guarded military headquarters in East Prussia. Like all his other outposts, Hitler had named it—appropriately enough—“Wolf’s Lair.”
Stauffenberg entered the large, concrete building while the conference was in session. He placed his yellow briefcase next to Hitler—who was standing with his generals at a heavy oaken table. Then he excused himself to take an “urgent” phone call.
At 12:42 p.m. on July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg’s briefcase bomb erupted.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ERNEST BORGNINE, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, Robert Ryan, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THE WILD BUNCH (MOVIE), THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WILLIAM HOLDEN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on October 29, 2025 at 12:10 am
In the classic 1969 Western, The Wild Bunch, the outlaw gang is pursued by a posse led by Deke Thornton (Robert Ryan), one of its own former members.
This triggers a furious exchange between the gang’s two leaders:
DUTCH ENGSTROM (Ernest Borgnine): Damn that Deke Thornton to hell!
PIKE BISHOP (William Holden): What would you do in his place? He gave his word.
DUTCH ENGSTROM: He gave his word to a railroad!
PIKE BISHOP: It’s his word!
DUTCH ENGSTROM: That’s not what counts! It’s who you give it to!
Where does loyalty leave off and conscience begin?
Specifically: If you’re a bodyguard for a man you know represents a genuine threat to democracy, what are your obligations to defend him? Should you be as willing to “take a bullet” for him as for someone you truly admire?
In October, 2016, Kerry O’Grady, a senior agent in the Denver field office of the United States Secret Service, found herself facing such a quandary.
She had made a series of now-deleted postings on Facebook during the 2016 Presidential campaign saying that she supported Democrat Hillary Clinton and that she would not honor a federal law that prevents agents like her from publicly airing their political beliefs.

Kerry O’Grady
“As a public servant for nearly 23 years, I struggle not to violate the Hatch Act. So I keep quiet and skirt the median,” she wrote in one Facebook post. “To do otherwise can be a criminal offense for those in my position. Despite the fact that I am expected to take a bullet for both sides.”
She had also suggested on Facebook that she would not defend President Donald Trump should someone try to shoot him.
“But this world has changed and I have changed. And I would take jail time over a bullet or an endorsement for what I believe to be disaster to this country and the strong and amazing women and minorities who reside here. Hatch Act be damned. I am with Her [Hillary Clinton],” she wrote.
The Secret Service said in a statement that it could not comment on a specific personnel matter but that it was “aware of the postings and the agency is taking quick and appropriate action.
“All Secret Service agents and employees are held to the highest standards of professional and ethical conduct. Any allegations of misconduct are taken seriously and swiftly investigated.”


Secret Service agents
O’Grady was placed on administrative leave on January 28, 2017 and suspended with pay in February. The disciplinary action took months because of her high rank.
In March, 2019, she retired from the Secret Service.
During the next four years—2017 to 2021—Donald Trump came perilously close to becoming an absolute dictator.
Among his infamies and crimes:
- Repeatedly attacking the nation’s free press as “the enemy of the American people” for daring to report his growing list of crimes and disasters.
- Publicly siding with Russian dictator Vladimir Putin against American Intelligence agencies—such as the FBI, CIA and National Security Agency—which unanimously agreed that Russia had interfered with the 2016 Presidential election.
- Attacking and alienating America’s oldest allies, such as Canada and Great Britain.
- Firing FBI Director James Comey for refusing to pledge his personal loyalty to Trump—and continuing to investigate Russian subversion of the 2016 election.

Donald Trump
- Shutting down the Federal Government on December 22, 2018, because Democrats refused to fund his useless “border wall” between the United States and Mexico. An estimated 380,000 government employees were furloughed and another 420,000 were ordered to work without pay for 35 days.
- Allowing the deadly COVID-19 virus to ravage the country, killing 400,000 Americans by the time he left office.
- Repeatedly lying—while still in office and afterward—that the 2020 election had been “stolen” from him by massive voter fraud.
- Illegally trying to pressure state legislatures and governors to stop the certification of the vote that had made Joe Biden the president-elect.
- Inciting his followers to attack the Capitol Building where Senators and Representatives were meeting to count the Electoral Votes won by himself and Joseph Biden. His objective: Stop the count, which he knew would prove him the loser.
In the classic 1981 crime drama, Prince of the City, Danny Ciello (Treat Williams) turns federal witness against his fellow crime-committing police officers.
His mobbed-up cousin, Nick, warns him that the Mafia wants him dead—but that his greatest danger might come from the bodyguards now surrounding him: “Anyone can be hit. You know that. All a guard has to do is look the wrong way for a second.”
Had that happened while Trump occupied the White House, American democracy would not now be imperiled by a second Trump administration.
Bodyguards for Adolf Hitler faced no such qualms. Right up to the bitter end, with Russian forces only blocks from the Fuhrerbunker, they manned their posts, ready to die for the man who had led them, Germany and the world into the ultimate catastrophe.
Within six years, Hitler had:
- Ignited World War II in 1939 through his invasion of Poland.
- Directly or indirectly caused the deaths of 50 million people worldwide.
- Exterminated six million Jews throughout Eastern Europe and Russia through mass shootings or gassings in a vast system of concentration camps.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on June 13, 2024 at 12:12 am
On July 20, 1944, Colonel Claus Schenk von Stuaffenberg tried to assassinate Nazi Germany’s Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, with a time bomb.
Stauffenberg appeared at Hitler’s well-guarded military headquarters in East Prussia. Like all his other outposts, Hitler had named it—appropriately enough—“Wolf’s Lair.”
While a war conference was in session, he placed his yellow briefcase next to Hitler—who was standing with his generals at a heavy oaken table. Then he excused himself to take an “urgent” phone call.

“Wolf’s Lair”
But after Stauffenberg left the room, Colonel Heinz Brandt, who stood next to Hitler, found the briefcase blocking his legs. So he moved it—to the other side of the heavy oaken support, thus unknowingly shielding Hitler from the full blast.
At 12:42 p.m. on July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg’s briefcase bomb erupted.
Brandt died, as did two other officers and a stenographer. Hitler not only survived, but the plotters failed to seize the key broadcast facilities of the Reich.
This allowed Hitler to make a late-night speech to the nation, revealing the failed plot and assuring Germans that he was still alive. And he swore to flush out the “traitorous swine” who had tried to kill him.
Mass arrests quickly followed. Among the first victims discovered and executed was the conspiracy’s leader, Colonel Claus von Stauffenberg. Standing before a makeshift firing squad at midnight, he cried: “Long live our sacred Germany!”

Claus von Stauffenberg
At least 7,000 persons were arrested by the Gestapo. Of these, 4,980 were executed.
If the conspiracy had succeeded and Germany had surrendered in July or August, 1944, World War II would have ended eight to nine months earlier. This would have meant:
- The Russians—who didn’t reach Germany until April, 1945—could not have occupied the Eastern part of the country.
- Millions of East Germans would have been spared the misery of living under Communist rule for 44 years.
- Many of the future conflicts between the United States and the Soviet Union over access to West Berlin and/or West Germany would have been prevented.
- Untold numbers of Holocaust victims would have survived because the concentration camps would have been shut down far earlier.
Yet history notes other tyrants whose evil reigns ended prematurely—such as that of Gaius Caligula.
Caligula became Emperor of Rome in 37 A.D. after succeeding the Emperor Tiberius, his uncle.
For three years, he held—and exercised—life-or-death power over the citizens of Italy and beyond. His attitude toward humanity was best summed up by his remark: “Bear in mind that I can treat anyone exactly as I please.”

Gaius Caligula
Carole Raddato from FRANKFURT, Germany, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Among his litany of crimes, according to his biographer, Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus:
- He forced parents to attend the executions of their sons, sending a litter for one man who pleaded ill health. He invited another to dinner immediately after witnessing the execution, and trying to rouse him to gaiety by a great show of affability.
- He watched for several successive days as the manager of his gladiatorial shows was beaten with chains, and ordered him killed only when he was disgusted at the stench of his putrefied brain.
- He appeared at the temple of Castor and Pollux to be worshiped as Jupiter Latiaris.
- He lived in incest with all his three sisters. At a large banquet he placed each of them in turn below him, while his wife reclined above.
- He intended to promote his favorite racehorse, Incitatus (“Swift”), to consul.
Like all Roman emperors, Caligula was constantly protected by the Praetorian Guard, an elite unit of the Roman army comprised of tough legionnaires—especially German ones.
There had not been an assassination of a Roman emperor since the death of Julius Caesar almost 100 years earlier.
The assassins in that case had been motivated by a mixture of
- Personal animosity toward Caesar’s increasing arrogance and
- Genuine fears that he intended to abolish the Roman Republic and set himself up as a dictator.
And Caligula intended to keep a similar fate from overtaking him.
For all his cruelty and egomania, the trait that finally destroyed Caligula was his joy in humiliating others.
Among those he taunted was Cassius Chaerea, a member of his own bodyguard.
Two different historians give two different motives for his decision to assassinate Caligula.
The Jewish historian Josephus claimed that Chaerea was a “noble idealist” deeply committed to “Republican liberties.”
But Suetonius wrote that Caligula considered Chaerea effeminate because of a weak voice and gave him such mocking watchwords as “Priapus” and “Venus.” Whenever Caligula had Chaerea kiss his ring, the emperor would “hold out his hand to kiss, forming and moving it in an obscene fashion.”
On January 22 41 A.D. Chaerea and several other bodyguards hacked Caligula to death with swords before other guards could save him.
The assassination attempts on Adolf Hitler and the successful assassination of Gaius Caligula demonstrate that the greatest danger facing a tyrant is people who:
- Are in frequent and highly personal contact with him; and
- Keep their animosity toward him a secret—until the moment they wish to strike.
Had Secret Service agent Kerry O’Grady kept her revulsion toward Donald Trump to herself, she might now be hailed as an American traitor—or as democracy’s savior.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on June 12, 2024 at 12:08 am
Where does loyalty leave off and conscience begin?
Specifically: If you’re a bodyguard for a man you know represents a genuine threat to democracy, what are your obligations to defend him? Should you be as willing to “take a bullet” for him as for someone you truly admire?
Members of Adolf Hitler’s bodyguard faced no such qualms. Right up to the bitter end, with Russian forces only blocks from the Fuhrerbunker, they manned their posts, ready to die for the man who had led them—and Germany—into the ultimate catastrophe.
They made Hitler a closely-guarded target.
He was surrounded by fanatical bodyguards who were expert marksmen. He often wore a bulletproof vest and a cap lined with three pounds of laminated steel.
But his single greatest protection—he claimed—was an instinct for danger. He would suddenly change his schedule—to drop in where he was least expected. Or suddenly depart an event where he was expected to stay a long time.

Adolf Hitler
It wasn’t Hitler’s bodyguards who posed a threat to his life. It was the colonels and generals of the German General Staff.
On August 20, 1934, members of the German army, navy and air force were required to swear the “Law On The Allegiance of Civil Servants and Soldiers of the Armed Forces.”
Whereas members of the armed forces had previously sworn loyalty to Germany, the new law required them to swear an oath of loyalty to Hitler personally.
In coming years, this would prove a deadly trap for many German officers—forcing them to choose between betraying a sacred oath and remaining loyal to a man who was clearly driving Germany to ruin.
For those officers who could not abide Germany’s coming destruction, the choice was simple: Hitler had to go.
A series of assassination attempts were made against Hitler. All of them involved time-bombs. And all of the would-be assassins were members of the German General Staff.
In one case, a bomb secretly stashed aboard Hitler’s plane failed to explode. In another, an officer who had a bomb strapped to himself unexpectedly found his scheduled meeting with Hitler called off. He had to rush into a bathroom to defuse the bomb before it exploded.
Hitler came closest to death on July 20, 1944.
Colonel Claus Schenk von Stuaffenberg was the driving force in a plot to assassinate Hitler with a time bomb.

Claus von Stauffenberg
He had served with the Wehrmacht in Poland (1939), France (1940) and the Soviet Union (1941). While serving in Tunisa, he was seriously wounded on April 7, 1943, when Allied fighters strafed his vehicle. He lost his left eye, right hand and two fingers of his left hand after surgery.
For most of his fellow officers, the motive was craven: The “happy time” of German victories was over. Germany was losing the war it had unleashed on the world in 1939—and now they feared the worst.
This was especially true now that the numerically superior forces of the Soviet Union had gone onto the offensive.

The Wehrmacht in Russia
The Wehrmacht and Schutzstaffel (SS) had killed millions of Russians. Many had died in combat. Others had been murdered as captives. Still more had been allowed to die by starvation and exposure to the notorious Russian winter.
For Stauffenberg, there was another reason: His disgust at the horrors he had seen committed by his fellow Wehrmacht soldiers upon defenseless POW’s and civilians in Russia.
Thus, Stauffenberg—more than many Germans—knew firsthand the vengeance his country could expect if the “Thousand-Year Reich” fell. Something must be done, he believed, to prove to the world that not all Germans—even members of the Wehrmacht—were criminals.
Most of the conspirators wanted to arrest Hitler and surrender to British and American forces—well before the much-feared Russians gained a toehold in Germany. Stauffenberg didn’t want to arrest Hitler; he wanted to kill him. A live Hitler might eventually be rescued by his Nazi colleagues.
Stauffenberg intended to carry his bomb—hidden in a briefcase—into a “Hitler conference” room packed with military officers. Rigged with a time-fuse, it would be left there while he found an excuse to leave. After the explosion, he would phone one of his fellow conspirators with the news.
Stauffenberg intended to direct the new government that would replace that of the Nazis—and open peace talks with the British and Americans. With Hitler dead, the coup—“Operation Valkyrie”—would be on.
Anti-Nazi conspirators would seize control of key posts of the government. They would inform the British and Americans of Germany’s willingness to surrender. Provided, of course, that the vengeance-seeking Russians did not have a say in its postwar future.
On July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg appeared at Hitler’s well-guarded military headquarters in East Prussia. Like all his other outposts, Hitler had named it—appropriately enough—“Wolf’s Lair.”
Stauffenberg entered the large, concrete building while the conference was in session. He placed his yellow briefcase next to Hitler—who was standing with his generals at a heavy oaken table. Then he excused himself to take an “urgent” phone call.
At 12:42 p.m. on July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg’s briefcase bomb erupted.
2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THE WILD BUNCH (MOVIE), THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WORLD WAR 11, X
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on June 11, 2024 at 12:22 am
In the classic 1969 Western, The Wild Bunch, the outlaw gang is pursued by a posse led by Deke Thornton, one of its own former members.
This triggers a furious exchange between the gang’s two leaders:
DUTCH ENGSTROM: Damn that Deke Thornton to hell!
PIKE BISHOP: What would you do in his place? He gave his word.
DUTCH ENGSTROM: He gave his word to a railroad!
PIKE BISHOP: It’s his word!
DUTCH ENGSTROM: That’s not what counts! It’s who you give it to!
Where does loyalty leave off and conscience begin?
Specifically: If you’re a bodyguard for a man you know represents a genuine threat to democracy, what are your obligations to defend him? Should you be as willing to “take a bullet” for him as for someone you truly admire?
In October, 2016, Kerry O’Grady, a senior agent in the Denver field office of the United States Secret Service, found herself facing such a quandary.
She had made a series of now-deleted postings on Facebook during the 2016 Presidential campaign saying that she supported Democrat Hillary Clinton and that she would not honor a federal law that prevents agents like her from publicly airing their political beliefs.

Kerry O’Grady
“As a public servant for nearly 23 years, I struggle not to violate the Hatch Act. So I keep quiet and skirt the median,” she wrote in one Facebook post. “To do otherwise can be a criminal offense for those in my position. Despite the fact that I am expected to take a bullet for both sides.”
She had also suggested on Facebook that she would not defend President Donald Trump should someone try to shoot him.
“But this world has changed and I have changed. And I would take jail time over a bullet or an endorsement for what I believe to be disaster to this country and the strong and amazing women and minorities who reside here. Hatch Act be damned. I am with Her [Hillary Clinton],” she wrote.
The Secret Service said in a statement that it could not comment on a specific personnel matter but that it was “aware of the postings and the agency is taking quick and appropriate action.
“All Secret Service agents and employees are held to the highest standards of professional and ethical conduct. Any allegations of misconduct are taken seriously and swiftly investigated.”

Secret Service agents
O’Grady was placed on administrative leave on January 28, 2017 and suspended with pay in February. The disciplinary action took months because of her high rank.
In March, 2019, she retired from the Secret Service.
During the next four years—2017 to 2021—Donald Trump came perilously close to becoming an absolute dictator.
Among his infamies and crimes:
- Repeatedly attacking the nation’s free press as “the enemy of the American people” for daring to report his growing list of crimes and disasters.
- Publicly siding with Russian dictator Vladimir Putin against American Intelligence agencies—such as the FBI, CIA and National Security Agency—which unanimously agreed that Russia had interfered with the 2016 Presidential election.
- Attacking and alienating America’s oldest allies, such as Canada and Great Britain.
- Firing FBI Director James Comey for refusing to pledge his personal loyalty to Trump—and continuing to investigate Russian subversion of the 2016 election.

Donald Trump
- Shutting down the Federal Government on December 22, 2018, because Democrats refused to fund his useless “border wall” between the United States and Mexico. An estimated 380,000 government employees were furloughed and another 420,000 were ordered to work without pay for 35 days.
- Allowing the deadly COVID-19 virus to ravage the country, killing 400,000 Americans by the time he left office.
- Repeatedly lying—while still in office and afterward—that the 2020 election had been “stolen” from him by massive voter fraud.
- Illegally trying to pressure state legislatures and governors to stop the certification of the vote that had made Joe Biden the president-elect.
- Inciting his followers to attack the Capitol Building where Senators and Representatives were meeting to count the Electoral Votes won by himself and Joseph Biden. His objective: Stop the count, which he knew would prove him the loser.
In the classic 1981 crime drama, Prince of the City, Danny Ciello (Treat Williams) turns federal witness against his fellow crime-committing police officers.
His mobbed-up cousin, Nick, warns him that the Mafia wants him dead—but that his greatest danger might come from the bodyguards now surrounding him: “Anyone can be hit. You know that. All a guard has to do is look the wrong way for a second.”
Had that happened while Trump occupied the White House, American democracy would not now be imperiled by a second Trump administration.
Bodyguards for Adolf Hitler faced no such qualms. Right up to the bitter end, with Russian forces only blocks from the Fuhrerbunker, they manned their posts, ready to die for the man who had led them, Germany and the world into the ultimate catastrophe.
Within six years, Hitler had:
- Ignited World War II in 1939 through his invasion of Poland.
- Directly or indirectly caused the deaths of 50 million people worldwide.
- Exterminated six million Jews throughout Eastern Europe and Russia through mass shootings or gassings in a vast system of concentration camps.
ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AP, BACKING HITLER: CONSENT AND COERCION IN NAZI GERMANY, BUZZFEED, CANADA, CBS NEWS, CNN, COMMUNISTS, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOZ, DONALD J. TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ECONOMY, EMPLOYMENT, EUROPEAN UNION, FACEBOOK, FBI, GESTAPO, JAMES COMEY, MEDIA, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NAZI ATROCITIES, NBC NEWS, NEWSWEEK, NPR, PARDON, POLITICO, RAW STORY, REPUBLICANS, REUTERS, ROBERT GELLATELY, RUDOLPH GIULIANI, SALON, SARAH HUCKABEE SANDERS, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, TARIFFS, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE WASHINGTON POST, TIME, TRADE WAR, TWITTER, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNEMPLOYMENT, UPI, USA TODAY, WEHRMACHT, WEST GERMANY
In Bureaucracy, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Politics, Social commentary on May 3, 2019 at 12:22 am
Everyone knows how World War II ended for Nazi Germany: With its Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, dead, and its capital city of Berlin in ruins.
Casualty figures range from 4.3 to 5.3 million dead Germans.
And for 44 years—from May 7, 1945, until November 9, 1989—Berlin was a divided city and Germany a divided nation. The Soviet Union ruled the eastern half. Germans—backed up by American military forces—ruled the western half.
Yet before all this unhappiness descended on the Fatherland, the vast majority of Germans enjoyed what they called “The Happy Time.”
This period began on January 30, 1933, when Adolf Hitler became Chancellor—and lasted until June 22, 1941.
For most Germans, those years—and especially the year between June, 1940, and June, 1941–were a time of prosperity and joy.
According to Robert Gellately’s 2002 landmark study, Backing Hitler: Consent and Coercion in Nazi Germany, the Nazis operated a highly popular dictatorship. They didn’t try to cow people into submission. Instead, they set out to win converts by building on popular images, cherished ideals and long-held phobias.
And their efforts succeeded. The Gestapo owed its fearsome success to ordinary German citizens who voluntarily reported on “enemies” within their midst. These citizens saw themselves as patriots.
Nor, as has long been believed, were Nazi atrocities carried out in secret. From the media, Germans learned about the Nazis’ brutal campaign against the Jews, the concentration camps, and the Nazis’ radical approaches to “law and order.”
But as far as everyday Germans were concerned:
- The streets were clean and peaceful.
- Employment was high.
- The Communists and Jews were being locked up.
- The trouble-making unions were gone.
- Germany was once again “taking its rightful place” among ruling nations, after its catastrophic defeat in World War 1.
The height of “The Happy Time” came in June, 1940. In just six weeks, the Wehrmacht accomplished what the German army hadn’t in four years during World War 1: The total defeat of its longtime enemy, France.

Frenzied Germans greet Adolf Hitler
Suddenly, French clothes, perfumes, delicacies, paintings and other “fortunes of war” came pouring into the Fatherland. (Reichsmarshall Herman Goring, head of the Luftwaffe—air force—amassed his own private air collection from French museums.)
Most Germans believed der Krieg—“the war”—was over, and only good times lay ahead.
But Adolf Hitler had other plans.
On June 22, 1941, three million Wehrmacht soldiers slashed their way into the Soviet Union. The Third Reich was now locked in a death-struggle with a nation even more powerful than itself.

German soldiers in the Soviet Union
And then, on December 11, 1941—four days after Germany’s ally, Japan, attacked Pearl Harbor—Hitler declared war on the United States.
“The Happy Time” for Germans was over. Only prolonged disaster lay ahead.
Now, fast forward 77 years to the America of President Donald J. Trump. According to an official White House statement entitled “American Greatness,” issued on June 4, 2018:

Donald Trump
“Nearly 3 million jobs have been created since President Trump took office. The unemployment rate has dropped to 3.8, the lowest rate since April 2000, and job openings have reached 6.6 million, the highest level recorded. President Trump has restored confidence in the American economy, with confidence among both consumers and businesses reaching historic highs.”
Much of this jobs growth, however, was already underway during the closing years of the Obama administration. But that hasn’t stopped Trump from taking credit for it.
White House Press Secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders doubtless spoke for millions of Trump supporters when she said, on June 4, 2018: “Since taking office, the President has strengthened American leadership, security, prosperity, and accountability. And as we saw from Friday’s jobs report, our economy is stronger, Americans are optimistic, and business is booming.
“The American people do not believe this strong economy is fantasy or unrealistic.”
Many Congressional Republicans have echoed this: The American people care only about the economy—and how well-off they are.
Only five days earlier—on May 31, 2018—the Trump administration had announced it would put steel and aluminum tariffs on longtime American allies Canada, Mexico and the European Union (EU).
Mexico, Canada and the EU immediately vowed to retaliate. For Americans, this will mean higher prices on such items as beer, baseball bats and cars. The EU has threatened to impose tariffs on motorcycles, bourbon whiskey, Levi’s jeans, peanut butter and cranberries.
A disastrous global trade war could be the ultimate result.
On June 4, Trump claimed, in a tweet: “As has been stated by numerous legal scholars, I have the absolute right to PARDON myself….”
And, making clear how far above the law he thinks Trump is, his attorney, Rudolph Giuliani, told the Huffington Post on June 3: “In no case can he be subpoenaed or indicted. I don’t know how you can indict while he’s in office. No matter what it is.
“If he shot [former FBI director] James Comey, he’d be impeached the next day. Impeach him, and then you can do whatever you want to do to him.”
The Germans made a similar devil’s-bargain with Hitler—and paid dearly for it. Americans, by supporting Trump—or at least not opposing him—have made a similar devil’s-bargain.
And such bargains always end with the devil winning.
ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALBANIA, ALTERNET, ANDREI CHERNY, AP, BERLIN AIRLIFT, BULGARIA, BUZZFEED, CAMILLUS, CBS NEWS, CNN, CONTAINMENT, CROOKS AND LIARS, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DAILY KOZ, EAST GERMANY, FACEBOOK, FALISCIA, FRANCE, FRANKLIN D. ROOSEVELT, GAIL “HAL” HALVORSEN, GREAT BRITAIN, HARRY S. TRUMAN, HUNGARY, IRON CURTAIN, JOSEPH STALIN, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEWSWEEK, NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI, NPR, POLAND, POLITICO, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROMANIA, ROME, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, THE ATLANTIC, THE CANDY BOMBERS, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE WASHINGTON POST, TIME, TWITTER, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES, UPI, USA TODAY, WEST BERLIN, WILLIE "THE WHIP" TUNNER, WORLD WAR 11, YUGOSLAVIA
In Bureaucracy, History, Military, Politics, Social commentary on May 2, 2019 at 12:04 am
In June, 1948, Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin was determined to drive the Western occupying powers out of Berlin—and of West Germany.
On June 19, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies’ railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control.
At that time, West Berlin had only 36 days’ worth of food and 45 days’ worth of coal. And the United States had only 8,973 Americans stationed in Berlin. British forces totaled 7,606, and French forces 6,100.
Russian forces in Berlin and East Germany outnumbered them 62 to 1.
The United States seemed to face a choice between all-out war with the Soviet Union—or appeasing its growing aggression in Eastern Europe.
Fortunately, a third choice was found. It became known as the Berlin Airlift.
This was carried out primarily by the United States and Great Britain. Other Western powers taking part in this operation included France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand and South Africa.
Starting on June 24, 1948, the Berlin Airlift aimed to supply the city’s two and a half million residents with food and energy supplies.
There was no guarantee that such an operation could succeed–at least, not in the long run. Since 1903, airplanes had been used to carry out surveillance, engage in dogfights or bomb cities. But airlifts—flying supplies to stranded people—had proven dismal failures.
At first, the Berlin Airlift worked haphazardly. Pilots flew themselves to exhaustion to meet the needs of those they had relentlessly bombed just three years ago.
Then Major General William “Willie the Whip” Tunner took charge—and brought a totally mechanized approach to the drops:
- Pilots must fly strictly by instruments, even when visibility was excellent.
- Planes could no longer circle over Berlin. Each plane would have only one chance to land in Berlin—or must return to its base if it missed its approach.
- Every 90 seconds, a plane was to take off or land.
Just keeping Berliners alive demanded 4,000 tons of supplies each day. Each plane was thus overloaded by 10 tons. Pilots flew literally round the clock. When fog rolled in that winter, visibility was reduced to zero. Twenty-eight Americans died in crashes.

A Douglas C-54 Skymaster lands at Berlin’s Templehof Airport
Germans were impressed with American efficiency, but knew that, in the eyes of most of their American occupiers, they were pariahs. They had waged an aggressive war and exterminated millions of helpless men, women and children in concentration camps.
They were glad the Allies were keeping them alive, but felt they were pawns in a global chess game between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Then fate took a hand.
An Army Air Force pilot named Gail “Hal” Halvorsen impulsively decided to drop a series of small, hand-made parachutes of candies to Berlin’s children.
When General Tunner learned of this, he instantly realized its worth as a morale booster to Berliners. He ordered Halvorsen to continue the drops.

Gail “Hal” Halvorsen
Other pilots followed Halvorsen’s example. Soon Berlin’s children were lining up by the thousands, hoping to grab one of the candy-filled parachutes made from handkerchiefs or strips of clothing.
When the press learned of the drops, the story became a worldwide sensation. Back in the United States, Americans mailed literally tons of candy to Germany for distribution to Berlin’s children.
“The candy bombers” became the most beloved Americans in Berlin. And Halvorsen became the most beloved of them all. On October 3, 1948, when his plane landed in Berlin during a pouring storm, 700 children greeted him on the tarmac for “Lieutenant Gail Halvorsen Day.”
Among the letters he received from Berlin’s children:
Dear Uncle Wiggly Wings,
When yesterday I came from school, I had the happiness to get one of your sweet gifts….You cannot think how big the joy was….My brother and parents stood about me when I opened the strings and fetched out all the chocolate.
Dear Candy Bomber,
…How lucky I was last Sunday. I played at a ruin with some friends of mine opposite our house. Suddenly we saw about ten white parachutes coming out of the sky! One of them set down on the roof of our house. There were three stripes chocolate in the parachute….I want to thank you for your love to the German kids….
From 10-year-old Helma Lurch came this tribute:
Take care of yourself, and remember us children and we will remember you our whole life.
Adults as well as children responded emotionally to the candy drops—and “the candy bombers” responsible for them. When a plane crashed, killing two American lieutenants, residents of the neighborhood memorialized them with a plaque: “Once we were enemies yet you now gave your lives for us. We are doubly in your debt.”
The Airlift ended on May 12, 1949, when Stalin finally accepted defeat and ended the blockade.
“As [Halvorsen] came to represent the Airlift and America to the Berliners,” writes Andrei Cherney in his definitive book, The Candy Bombers, “through him America became a country that cared enough about the defeated Germans to…deliver candy to children, an act without any…ulterior motive, a gift of plain compassion.”
In 1948, that act forged a solid bond—which still exists—between Germany and the United States.
ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALBANIA, ALTERNET, AP, BERLIN AIRLIFT, BULGARIA, BUZZFEED, CAMILLUS, CBS NEWS, CNN, CONTAINMENT, CROOKS AND LIARS, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DAILY KOZ, EAST GERMANY, FACEBOOK, FALISCIA, FRANCE, FRANKLIN D. ROOSEVELT, GREAT BRITAIN, HARRY S. TRUMAN, HUNGARY, IRON CURTAIN, JOSEPH STALIN, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEWSWEEK, NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI, NPR, POLAND, POLITICO, RAW STORY, REUTERS, ROMANIA, ROME, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DISCOURSES, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE WASHINGTON POST, TIME, TWITTER, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES, UPI, USA TODAY, WEST BERLIN, WORLD WAR ii, YUGOSLAVIA
In Bureaucracy, History, Military, Politics, Social commentary on May 1, 2019 at 12:03 am
Once again, it falls to Niccolo Machiavelli to reveal truths long forgotten—especially by those who subscribe only to the darkest arts.
In his most important book, The Discourses, he outlines the methods by which citizens of a republic can maintain their freedom.
In Book Three, Chapter 20, he offers this example of the power of humanity to win over even the most stubborn opponents:


Niccolo Machiavelli
Lorenzo Bartolini, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
“Camillus was besieging the city of the Faliscians, and had surrounded it….A teacher charged with the education of the children of some of the noblest families of that city [to ingratiate himself] with Camillus and the Romans, led these children…into the Roman camp.
“And presenting them to Camillus [the teacher] said to him, ‘By means of these children as hostages, you will be able to compel the city to surrender.’
“Camillus not only declined the offer but had the teacher stripped and his hands tied behind his back….[Then Camillus] had a rod put into the hands of each of the children…[and] directed them to whip [the teacher] all the way back to the city.
“Upon learning this fact, the citizens of Faliscia were so much touched by the humanity and integrity of Camillus, that they surrendered the place to him without any further defense.
“This example shows that an act of humanity and benevolence will at all times have more influence over the minds of men than violence and ferocity. It also proves that provinces and cities which no armies…could conquer, have yielded to an act of humanity, benevolence, chastity or generosity.”
Americans put this lesson to use in 1948 in the skies over Berlin.
When Nazi Germany fell to the Allies in May, 1945, the country was divided into four zones of occupation—one for each of the occupying powers: The United States, Great Britain, France and the Soviet Union.
Within the fledgling administration of President Harry S. Truman, many believed that a new era of peace had dawned between America and Russia.
But then grim reality intruded.
Adolf Hitler had invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. As a result, at least 20 million Soviet men, women and children died violently.
To expel the invasion and destroy Nazi Germany, Russian armies had advanced across a series of Eastern European countries. With the war over, Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin decided to protect the Soviet Union from a future German invasion.

Joseph Stalin
His solution: Occupy Eastern Europe with Red Army units as a buffer between Germany and the Soviet Union. Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Albania and Yugoslavia.
Stalin had promised President Franklin Roosevelt that he would withdraw his armies from these countries once Germany was defeated. And he would allow them to choose whatever form of government they desired.
But Stalin had no intention of living up to his promises. And backing him up were 10 to 13 million Red Army soldiers. The entire United States Army had been reduced to 552,000 men by February 1948.
Liberating the captive nations of Eastern Europe—as General George S. Patton wanted to do—would have plunged the United States into full-scale war against its World War II ally.
And by 1945, the Red Army was a formidable enemy: Of the 4.3 million dead and missing casualties suffered by the Wehrmacht, 85% of them occurred on the dreaded “Eastern front.”
So there was nothing the United States could do—short of all-out war—to “roll back” the “Iron Curtain” that had swept over Eastern Europe.
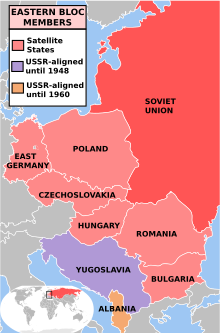
But Americans could—and did—draw a line in the sand. That line became known as the policy of “containment.”
And nowhere was the collision between the U.S.A and the U.S.S.R. more likely to ignite into full-scale war than in Berlin.
Between 1945 and 1948, the Soviets increased their pressure on Western forces occupying Berlin to leave the city. The Soviets already controlled East Germany; gaining control of the Western-held part of Berlin would likely be their first step toward overwhelming the rest of Germany.
And, after Germany, probably France—and as many other European countries as possible.
During the first two years of occupation the occupying powers of France, United Kingdom, United States, and the Soviet Union were not able to successfully negotiate a possible currency reform in Germany. Each of the Allies printed its own occupation currency.
Then, on June 20, 1948, the Bizonal Economic Council introduced the Deutsche mark to West Germany.
On June 24, 1945, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies’ railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. This meant a cutoff of food and energy supplies to Berlin’s two and a half million residents.
The United States faced a monumental crisis:
- Should it abandon West Berlin—and thus tempt the Soviet Union into further aggression?
- Should it match the puny Western military forces—outnumbered 62 to 1—against the massive Soviet military presence?
- If it chose to fight in Berlin, would this lead to nuclear war?
Fortunately for the Allies—and West Germany—a third choice was available besides war and appeasement.
It became known as the Berlin Airlift.
ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AP, BACKING HITLER: CONSENT AND COERCION IN NAZI GERMANY, BUZZFEED, CANADA, CBS NEWS, CNN, COMMUNISTS, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOZ, DONALD J. TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ECONOMY, EMPLOYMENT, EUROPEAN UNION, FACEBOOK, FBI, GESTAPO, JAMES COMEY, MEDIA, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NAZI ATROCITIES, NBC NEWS, NEWSWEEK, NPR, PARDON, POLITICO, RAW STORY, REPUBLICANS, REUTERS, ROBERT GELLATELY, RUDOLPH GIULIANI, SALON, SARAH HUCKABEE SANDERS, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, TARIFFS, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE WASHINGTON POST, TIME, TRADE WAR, TWITTER, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNEMPLOYMENT, UPI, USA TODAY, WEHRMACHT, WEST GERMANY
In Bureaucracy, Business, History, Law, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on June 12, 2018 at 12:39 am
Everyone knows how World War II ended for Nazi Germany: With its Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, dead, and its capital city of Berlin in ruins.
Casualty figures range from 4.3 to 5.3 million dead Germans.
And for 44 years—from May 7, 1945, until November 9, 1989—Berlin was a divided city and Germany a divided nation. The Soviet Union ruled the eastern half. Germans—backed up by American military forces—ruled the western half.
Yet before all this unhappiness descended on the Fatherland, the vast majority of Germans enjoyed what they called “The Happy Time.”
This period began on January 30, 1933, when Adolf Hitler became Chancellor—and lasted until June 22, 1941.
For most Germans, those years—and especially the year between June, 1940, and June, 1941–were a time of prosperity and joy.
According to Robert Gellately’s 2002 landmark study, Backing Hitler: Consent and Coercion in Nazi Germany, the Nazis operated a highly popular dictatorship. They didn’t try to cow people into submission. Instead, they set out to win converts by building on popular images, cherished ideals and long-held phobias.
And their efforts succeeded. The Gestapo owed its fearsome success to ordinary German citizens who voluntarily reported on “enemies” within their midst. These citizens saw themselves as patriots.
Nor, as has long been believed, were Nazi atrocities carried out in secret. From the media, Germans learned about the Nazis’ brutal campaign against the Jews, the concentration camps, and the Nazis’ radical approaches to “law and order.”
But as far as everyday Germans were concerned:
- The streets were clean and peaceful.
- Employment was high.
- The Communists and Jews were being locked up.
- The trouble-making unions were gone.
- Germany was once again “taking its rightful place” among ruling nations, after its catastrophic defeat in World War 1.
The height of “The Happy Time” came in June, 1940. In just six weeks, the Wehrmacht accomplished what the German army hadn’t in four years during World War 1: The total defeat of its longtime enemy, France.

Frenzied Germans greet Adolf Hitler
Suddenly, French clothes, perfumes, delicacies, paintings and other “fortunes of war” came pouring into the Fatherland. (Reichsmarshall Herman Goring, head of the Luftwaffe—air force—amassed his own private air collection from French museums.)
Most Germans believed der Krieg—“the war”—was over, and only good times lay ahead.
But Adolf Hitler had other plans.
On June 22, 1941, three million Wehrmacht soldiers slashed their way into the Soviet Union. The Third Reich was now locked in a death-struggle with a nation even more powerful than itself.

German soldiers in the Soviet Union
And then, on December 11, 1941—four days after Germany’s ally, Japan, attacked Pearl Harbor—Hitler declared war on the United States.
“The Happy Time” for Germans was over. Only prolonged disaster lay ahead.
Now, fast forward 77 years to the America of President Donald J. Trump. According to an official White House statement entitled “American Greatness,” issued on June 4:

Donald Trump
“Nearly 3 million jobs have been created since President Trump took office. The unemployment rate has dropped to 3.8, the lowest rate since April 2000, and job openings have reached 6.6 million, the highest level recorded. President Trump has restored confidence in the American economy, with confidence among both consumers and businesses reaching historic highs.”
Much of this jobs growth, however, was already underway during the closing years of the Obama administration. But that hasn’t stopped Trump from taking credit for it.
White House Press Secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders doubtless spoke for millions of Trump supporters when she said, on June 4: “Since taking office, the President has strengthened American leadership, security, prosperity, and accountability. And as we saw from Friday’s jobs report, our economy is stronger, Americans are optimistic, and business is booming.
“The American people do not believe this strong economy is fantasy or unrealistic.”
Many Congressional Republicans have echoed this: The American people care only about the economy—and how well-off they are.
Only five days earlier—on May 31—the Trump administration had announced it would put steel and aluminum tariffs on longtime American allies Canada, Mexico and the European Union (EU).
Mexico, Canada and the EU immediately vowed to retaliate. For Americans, this will mean higher prices on such items as beer, baseball bats and cars. The EU has threatened to impose tariffs on motorcycles, bourbon whiskey, Levi’s jeans, peanut butter and cranberries.
A disastrous global trade war could be the ultimate result.
On June 4, Trump claimed, in a tweet: “As has been stated by numerous legal scholars, I have the absolute right to PARDON myself….”
And, making clear how far above the law he thinks Trump is, his attorney, Rudolph Giuliani, told the Huffington Post on June 3: “In no case can he be subpoenaed or indicted. I don’t know how you can indict while he’s in office. No matter what it is.
“If he shot [former FBI director] James Comey, he’d be impeached the next day. Impeach him, and then you can do whatever you want to do to him.”
The Germans made a similar devil’s-bargain with Hitler—and paid dearly for it. Americans, by supporting Trump—or at least not opposing him—have made a similar devil’s-bargain.
And such bargains always end with the devil winning.







2016 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, 2020 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION, ABC NEWS, ADOLF HITLER, ALTERNET, AMERICABLOG, AP, BABY BOOMER RESISTANCE, BBC, BLOOMBERG, BUZZFEED, CASSIUS CHAEREA, CBS NEWS, CIA, CLAUSS VON STAUFFENBERG, CNN, COVID-19, CROOKS AND LIARS, DAILY KOS, DONALD TRUMP, EAST GERMANY, ERNEST BORGNINE, FBI, FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN, FIVETHIRTYEIGHT, GAIUS CALIGULA, GAIUS SUETONIUS TRANQUILLUS, GERMAN GENERAL STAFF, HARPER’S MAGAZINE, HITLER LOYALTY OATH, HOLOCAUST, HUFFINGTON POST, JANUARY 6 COUP ATTEMPT, JOSEPH BIDEN, JOSEPHUS, JULIUS CAESAR, KERRY O’GRADY, MEDIA MATTERS, MEXICO, MOTHER JONES, MOVEON, MSNBC, NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY, NAZI GERMANY, NBC NEWS, NEW REPUBLIC, NEWSDAY, NEWSWEEK, NPR, OPERATION VALKYRIE, PBS NEWSHOUR, POLITICO, POLITICUSUSA, PRINCE OF THE CITY (MOVIE), RAW STORY, REUTERS, Robert Ryan, SALON, SEATTLE TIMES, SLATE, SOVIET UNION, SS, TALKING POINTS MEMO, THE ATLANTIC, THE CHICAGO SUN-TIMES, THE CHICAGO TRIBUNE, THE DAILY BEAST, THE DAILY BLOG, THE GUARDIAN, THE HILL, THE HUFFINGTON POST, THE INTERCEPT, THE LOS ANGELES TIMES, THE NATION, THE NEW REPUBLIC, THE NEW YORK TIMES, THE NEW YORKER, THE VILLAGE VOICE, THE WASHINGTON POST, THE WILD BUNCH (MOVIE), THINKPROGRESS, TIME, TRUTHDIG, TRUTHOUT, TWO POLITICAL JUNKIES, U.S. NEWS & WORLD REPORT, UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION, UNITED STATES SECRET SERVICE, UPI, USA TODAY, VLADIMIR PUTIN, WEST BERLIN, WILLIAM HOLDEN, WORLD WAR 11, X
TYRANTS AND THEIR BODYGUARDS: PART THREE (END)
In Bureaucracy, History, Law Enforcement, Military, Politics, Social commentary on October 31, 2025 at 12:10 amOn July 20, 1944, Colonel Claus Schenk von Stuaffenberg tried to assassinate Nazi Germany’s Fuhrer, Adolf Hitler, with a time bomb.
Stauffenberg appeared at Hitler’s well-guarded military headquarters in East Prussia. Like all his other outposts, Hitler had named it—appropriately enough—“Wolf’s Lair.”
While a war conference was in session, he placed his yellow briefcase next to Hitler—who was standing with his generals at a heavy oaken table. Then he excused himself to take an “urgent” phone call.
“Wolf’s Lair”
But after Stauffenberg left the room, Colonel Heinz Brandt, who stood next to Hitler, found the briefcase blocking his legs. So he moved it—to the other side of the heavy oaken support, thus unknowingly shielding Hitler from the full blast.
At 12:42 p.m. on July 20, 1944, Stauffenberg’s briefcase bomb erupted.
Brandt died, as did two other officers and a stenographer. Hitler not only survived, but the plotters failed to seize the key broadcast facilities of the Reich.
This allowed Hitler to make a late-night speech to the nation, revealing the failed plot and assuring Germans that he was still alive. And he swore to flush out the “traitorous swine” who had tried to kill him.
Mass arrests quickly followed. Among the first victims discovered and executed was the conspiracy’s leader, Colonel Claus von Stauffenberg. Standing before a makeshift firing squad at midnight, he cried: “Long live our sacred Germany!”
Claus von Stauffenberg
At least 7,000 persons were arrested by the Gestapo. Of these, 4,980 were executed.
If the conspiracy had succeeded and Germany had surrendered in July or August, 1944, World War II would have ended eight to nine months earlier. This would have meant:
Yet history notes other tyrants whose evil reigns ended prematurely—such as that of Gaius Caligula.
Caligula became Emperor of Rome in 37 A.D. after succeeding the Emperor Tiberius, his uncle.
For three years, he held—and exercised—life-or-death power over the citizens of Italy and beyond. His attitude toward humanity was best summed up by his remark: “Bear in mind that I can treat anyone exactly as I please.”
Gaius Caligula
Carole Raddato from FRANKFURT, Germany, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Among his litany of crimes, according to his biographer, Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus:
Like all Roman emperors, Caligula was constantly protected by the Praetorian Guard, an elite unit of the Roman army comprised of tough legionnaires—especially German ones.
There had not been an assassination of a Roman emperor since the death of Julius Caesar almost 100 years earlier.
The assassins in that case had been motivated by a mixture of
And Caligula intended to keep a similar fate from overtaking him.
For all his cruelty and egomania, the trait that finally destroyed Caligula was his joy in humiliating others.
Among those he taunted was Cassius Chaerea, a member of his own bodyguard.
Two different historians give two different motives for his decision to assassinate Caligula.
The Jewish historian Josephus claimed that Chaerea was a “noble idealist” deeply committed to “Republican liberties.”
But Suetonius wrote that Caligula considered Chaerea effeminate because of a weak voice and gave him such mocking watchwords as “Priapus” and “Venus.” Whenever Caligula had Chaerea kiss his ring, the emperor would “hold out his hand to kiss, forming and moving it in an obscene fashion.”
On January 22 41 A.D. Chaerea and several other bodyguards hacked Caligula to death with swords before other guards could save him.
The assassination attempts on Adolf Hitler and the successful assassination of Gaius Caligula demonstrate that the greatest danger facing a tyrant is people who:
Had Secret Service agent Kerry O’Grady kept her revulsion toward Donald Trump to herself, she might now be hailed as an American traitor—or as democracy’s savior.
Share this: